- Personal Stem cell therapy and stem cell banking is readily available across the United States, with both the safest techniques and highest quality standards. However, it is imperative to understand the difference between personal stem cells (autologous) and all the other options that are riskier and less transparent.
- People are receiving their own personal stem cells for regenerative purposes including orthopedic, autoimmune, neurological, cardiology, and pulmonary conditions, as well as cosmetic and wellness/bio-hacking purposes.
- Keep reading below to learn more about your personal stem cell options in the United States, why it is the safest and most effective offering, and the simple process on how to receive stem cell therapy in the United States today.
When I hear the phrase “fountain of youth,” my ears perk up. There are so many gimmicks out there trying to sell us on the dream of longevity but believe me when I say that stem cell therapy is no gimmick. That said, there’s a lot of confusion about stem cells, so we’re going to suss out the whole deal in this article – let’s go.
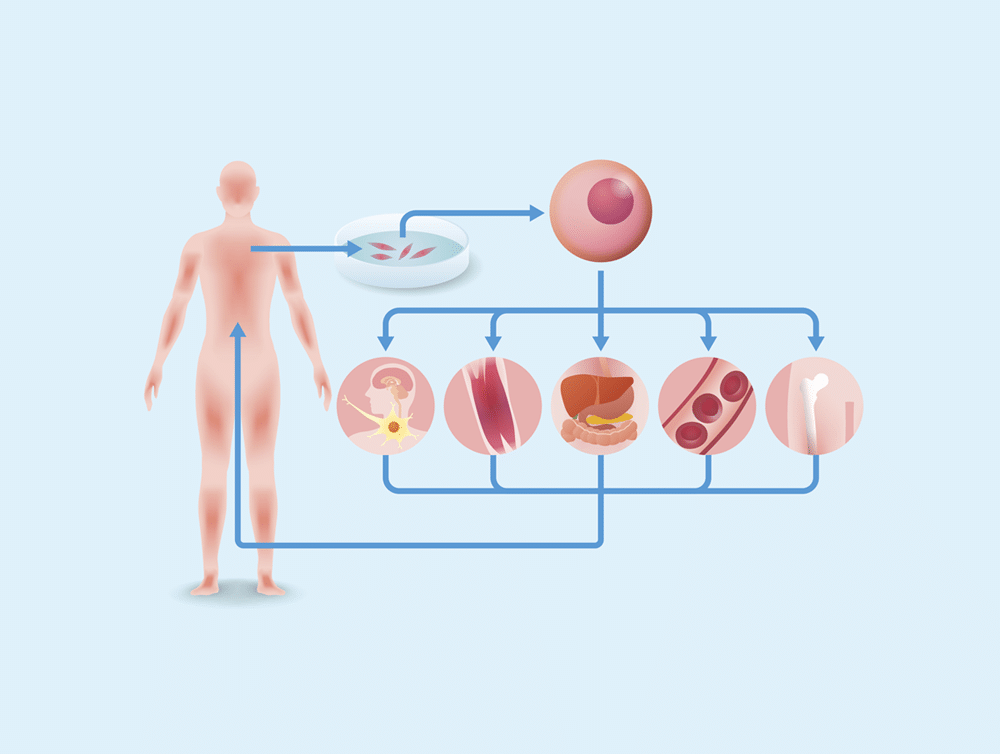
If you aren’t familiar, stem cells present one of today’s most promising therapeutic options for naturally healing injuries and hold potential for a range of other conditions. These unique cells can self-replicate, differentiate into other kinds of functional tissue, and send important cellular signals to other cells that ultimately promote recovery.
Due to regulatory ambiguity, however, stem cell therapy hasn’t been as widely available as most people would like.
In fact, athletes and those with plenty of cash to spend travel far and wide to places like China, Thailand, and Central and South America to shell out upwards of $40,000 to $100,000 for stem cell treatments promoted to help with aching, arthritic joints, neurodegenerative disorders, autoimmune conditions, or just for general wellness.
And if the price weren’t enough to deter you, many of these international stem cell treatments fail to clarify some of the most important factors that you need to think about when it comes to stem cell treatment, for instance:
- Are they using personal (autologous) cells or donor cells (allogenic)?
- Are they offering Live Stem Cell Count or total cell count that includes dead cells?
- Which type of live stem cells are they using? (mesenchymal, hematopoietic, cord, bone marrow or adipose-derived)
- Are the cells cultured expanded, fresh, or frozen?
- Are they offering treatments without stem cells (Exosomes, PRP, amniotic fluid)?
Despite the lack of clarity or complete understanding, people still seek regenerative treatments from these remote clinics in the hope of finding the Fountain of Youth.
Evolution of Stem Cell Research and Clinical Work – Not All Stem Cells Are The Same
One of the reasons many people feel “iffy” about stem cells is due to the shaky beginnings of stem cell research. In the beginning, stem cells were originally derived from embryos that had the potential to form teratomas or cancer, leading to warranted negative perceptions regarding stem cell treatments. However, what some people are unaware of is the fact that the clinical field has shifted towards using adult stem cells, and more specifically Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs), which have no risk of cancer formation and are available in nearly every tissue in the human body. The shift in working with MSCs has led to zero clinical work with embryonic stem cells in the last 15 years.
Today, there are three main sources of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) used in clinical applications[1]:
- Adipose-derived MSCs
- Bone marrow-derived MSCs
- Birth-Associated Tissues (cord tissue, cord blood, placenta) derived MSCs
Of these three sources of cells, all are adult MSCs, even though cord-derived MSCs are obtained after the birth of a newborn. The three cell sources all have adult characteristics and are pluripotent (able to form many tissues), as opposed to totipotent cells that can form any type of tissue (and sometimes uncontrollably – leading to cancer)[2][3].
Furthermore, all three types of MSCs have common traits associated with healing and repairing the body[4].
For example, these MSCs are all anti-inflammatory and can travel to sites of inflammation throughout the body. They are immunomodulatory (can up or down-regulate an immune response appropriately), they secrete pro-regenerative cytokines (fancy word for cell signals), and they can self-replicate or differentiate into functional tissue[5].
Your Personal Stem Cells (autologous) – The Safest Option
Now that we’ve cleared the air on the whole embryonic stem cell debacle, let’s consider something else; where are your stem cells coming from? When considering a cell source, it’s critical to ensure that the cell contains your own DNA (personal cell therapy).
Using cells from a donor (allogeneic) puts patients at risk of potential disease transmission, as the only screening donor cells undergo is for certain well-known viruses and rare genetic mutations. However, hundreds of viruses and prions (proteinaceous viruses hard to detect) go unscreened for.
Further, allogeneic cells don’t contain your own DNA. While they are deficient in MCH II markers, these cells still have MCH I markers (this is like driving with only a back license plate as opposed to one on the front and back)[6]. A deficiency in MCH II markers can cause your immune system to attack these cells, leading to graft-versus-host -disease (GVHD). GVHD occurs when the body attacks foreign DNA entering the recipient’s body and can result in chronic lifetime symptoms[7].
Which Autologous Cells Perform Best?
Okay, now that we’re clear that using your own stem cells is your best bet – which cell line should you go for?
Adipose and bone marrow MSCs are both great sources of autologous stem cells. However, bone marrow MSCs in patients over 40 tend to be older since these MSCs are responsible for making white blood cells within the immune system. On the other hand, adipose-derived MSCs do relatively little work over the course of their lives and are, therefore, still young and robust (measured by their telomeres) well into your 80s and 90s.
There are also 500 to 2,500 times more stem cells in your adipose tissue than in your bone marrow, making these cells a really attractive stem cell source for regenerative medical procedures[8].
What types of procedures?
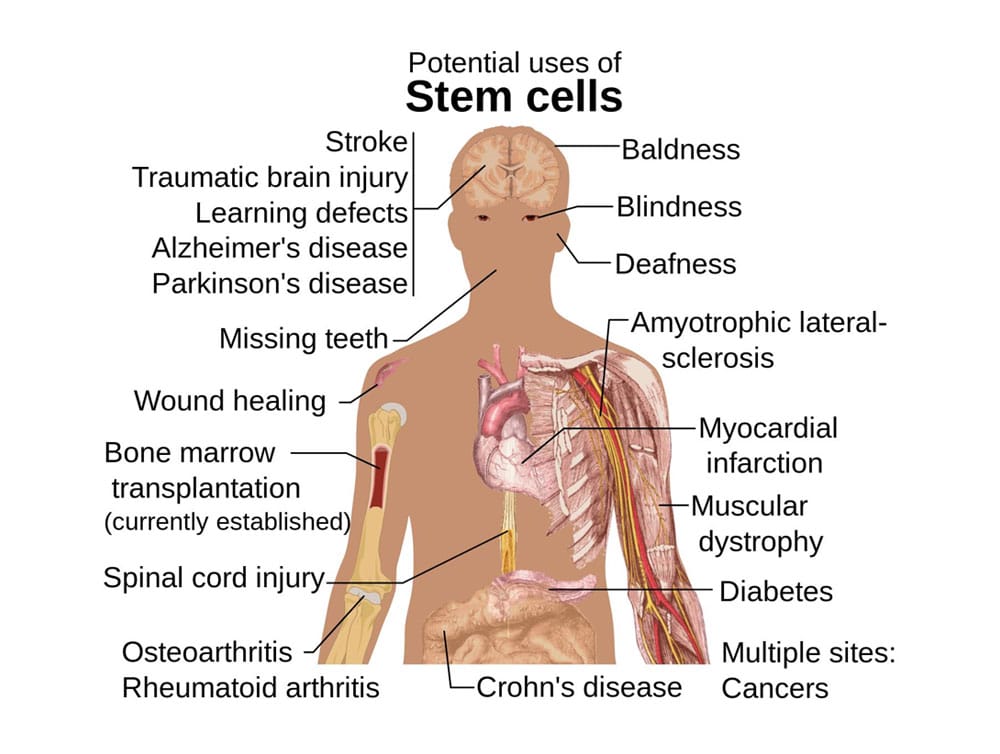
Mesenchymal Stem Cells are currently used in clinical trials or at regenerative medicine clinics for hundreds of uses. Including, but not limited to[9]:
Orthopedics: knee, hip, shoulder, and back arthritis, tendon or ligament damage, avoidance of joint replacement surgery
Autoimmune: Diabetes, Crohn’s, Rheumatoid Arthritis
Cosmetic: hair restoration, skin repair
Neurology: Autism, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Dementia, Stroke, Concussions, and Traumatic Brain Injury
Cardiology and Pulmonology: Heart Failure, Asthma, COPD
Bio-Hacking: Anti-aging/wellness, male and female sexual function, general body performance, and recovery
The power of personal stem cell banking
If your stem cells are currently not banked and cryopreserved, then the youngest personal cells you can access are those in your body today. Our stem cells are part of our body, meaning they age right along with us. Most of us had no option to properly store our youngest adult stem cells from our cord blood or tissue at birth. Currently, VitalCells is the only newborn stem cell bank that accurately stores and culture expands pure adult mesenchymal stem cells from the cord blood and cord tissue and actually provides children access to their youngest, adult stem cells throughout their life. They do this through their revolutionary processing, allowing clients to access billions of their own personal stem cells. There are only a couple million live stem cells on average natively available in the cord blood and cord tissue, so without VitalCells banking your newborn’s cord blood or tissue is severely limiting. Even though most adults today missed the opportunity to store their cells at birth, they still have the opportunity to work with the young cells within their adipose tissue[10].
And with American Cell Technology (ACT), the largest personal stem cell bank in the United States, you can unlock the powers and benefits of personal stem cell banking as ACT provides:
- Access to your youngest personal stem cells with your own DNA throughout your life.
- Availability of cells for numerous treatments through proprietary techniques to grow potentially billions of live Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs)
- Stem Cell retrieval options within 48 hours for emergency or on-demand requests
- Partnerships with leading regenerative medicine doctors nationally
- Avoidance of multiple stem cell extraction procedures as cells undergo cryogenic storage for access throughout their life
- Certainty of quality – Pure mesenchymal stem cells with accurate live stem counts and viability (health of the cells).
- Safety and security knowing that your cells are stored using the latest technology and with the highest standards in a FDA registered cGMP facility
- Elimination of any risk of your body rejecting the cells and therefore developing graft-versus-host disease (GVHD).
- Controlled processing that ensures healthy cells that must also successfully pass bioburden testing before shipment
With thousands of clinical trials underway and countless other treatments offered at regenerative medical clinics using personal mesenchymal stem cells, banking your personal stem cells can provide the ultimate healthcare security.
Can you receive stem cell therapy in the United States?
Absolutely. Personal stem cell therapy is available in the United States today. Due to less stringent marketing restrictions internationally and misinterpretations of stem cell therapy domestically with regulatory concerns, recent years have led to significant research and clinical advancement overseas. However, personal stem cell therapy within the United States has been active without a mouthpiece.
In fact, a recent ruling in federal court made it clear that physicians have the right to work with autologous stem cells in their medical practice and that these cells are not a drug and thus not within FDA oversight. The practice of medicine and surgical procedures don’t fall within the oversight of the FDA. For example, the FDA doesn’t approve knee replacement surgery. With the recent ruling in the federal court, access to peoples’ personal stem cells within the United States in the clinical setting has drastically increased as more physicians and clinics better understand their rights as medical professionals.
Access to Personal Stem Cell Banking and Therapy in the United States
..the complete and simple process
Most people like the idea of stem cell therapy but don’t want to bother with the whole process. Well, here’s the good news; it couldn’t be more straightforward.
Regenerative medicine clinics nationwide provide personal cell therapy and often offer personal stem cell banking services with American Cell Technology (ACT). The process is simple and more affordable than most think; here’s a breakdown:
#1. Talk to a doctor
Reach out to your stem cell doctor to see if you’re a candidate for personal cell therapy and stem cell banking. If you’re looking for a doctor near you, American Cell Technology (ACT) can recommend one of their partnered regenerative clinics across the United States.
#2. The procedure.
The procedure is simple and done under local anesthesia. The total time spent in the clinic can range from an hour to a few hours, depending on whether you elect only to stem cell bank or receive the same-day stem cell procedure.
For stem cell banking, a tablespoon of fat is drawn from the flank under local anesthesia in about 30 minutes. You are then free to go home after the procedure and return to receive your cells after six weeks from extraction.
For the same-day procedure, the medical practitioner will take an additional tablespoon of fat, isolate the stem cells from the fat and reinsert those stem cells within the body, either intravenously or direct injections into the joints or both.
Both options are outpatient procedures that may cause general bruising but will require no additional downtime.
#3. Stem cell processing
Stem cell processing takes place with American Cell Technology (ACT). Your medical professional overnight ships your adipose (fat) or bone marrow sample for processing. Once received, lab techs in an FDA-registered cGMP facility isolate your cells from the sample in a sterile, cleanroom environment. The cells then undergo a feeding process, allowing them to self-replicate naturally through the proprietary culture expansion process.
Depending on the banking program selected, ACT can grow up to billions of live mesenchymal stem cells through this process. Various bacteria, endotoxin, and sterility testing is standard service.
#4. Cryopreservation
Once your stem cells are grown to the desired amount, ACT cryopreserves your stem cells in time.
#5. Retrieving your cells with ease
Requesting your cells is easy through ACT’s customer support and ordering platform. Depending on your stem cell plan, you can potentially retrieve the cells within 48 hours. If on a standard plan, three weeks’ notice for cell retrieval is required. How you use your cells will be determined by you and your administering licensed practitioner.
And that’s it. Access to your stem cells when and where you need them couldn’t be easier.
Takeaway
The stem cell industry is constantly evolving, with ongoing research and clinical trials published daily. Taking the first steps in securing your future health is assuring that your youngest stem cells are banked and ready to do what they do best – heal your body from within.
Want to secure your future health? Get your stem cells banked today so you don’t have to worry about what happens tomorrow.
References
- Hass, Ralf, et al. “Different populations and sources of human mesenchymal stem cells (MSC): a comparison of adult and neonatal tissue-derived MSC.” Cell Communication and Signaling 9.1 (2011): 1-14.
- Andrews, Peter W. “From teratocarcinomas to embryonic stem cells.” Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences 357.1420 (2002): 405-417.
- Porada, Christopher D., Esmail D. Zanjani, and Graça Almeida-Porada. “Adult mesenchymal stem cells: a pluripotent population with multiple applications.” Current stem cell research & therapy 1.3 (2006): 365-369.
- Salari, Valentina, et al. “The anti-inflammatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells in epilepsy: Possible treatments and future perspectives.” International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21.24 (2020): 9683.
- Mizuno, Hiroshi, Morikuni Tobita, and A. Cagri Uysal. “Concise review: adipose?derived stem cells as a novel tool for future regenerative medicine.” Stem cells 30.5 (2012): 804-810.
- Cho, Patricia S., et al. “Immunogenicity of umbilical cord tissue–derived cells.” Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology 111.1 (2008): 430-438.
- https://www.pennmedicine.org/for-patients-and-visitors/patient-information/conditions-treated-a-to-z/graft-versus-host-disease
- Strioga, Marius, et al. “Same or not the same? Comparison of adipose tissue-derived versus bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem and stromal cells.” Stem cells and development 21.14 (2012): 2724-2752.
- Han, Yu, et al. “Mesenchymal stem cells for regenerative medicine.” Cells 8.8 (2019): 886.
- Burrow, Kimberley L., Judith A. Hoyland, and Stephen M. Richardson. “Human adipose-derived stem cells exhibit enhanced proliferative capacity and retain multipotency longer than donor-matched bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells during expansion in vitro.” Stem cells international 2017 (2017).