[tldr]
- Omega-3 is a type of essential fatty acid that powers your brain, heart, and joints.
- Your body can’t produce these fats on its own — you have to get them from a supplement or from food.
- There are different kinds of omega-3s: EPA and DHA. Most fish oil supplements contain a combination of EPA and DHA, since they each carry benefits and complement each other.
- You also want to make sure you have the right ratio of omega-3s and omega-6s (another type of essential fatty acid). For most people, the ideal ratio is 1:1.
- Since it’s not easy knowing whether you’ve got the balance right, taking an omega-3 supplement gives you piece of mind that you’ve covered your bases.
- Fish and krill oil supplements both contain EPA and DHA, but they each carry different benefits.
- Omega Krill Complex blends fish and krill oil together, so you get the high dose of EPA and DHA, coupled with maximum absorption.
[/tldr]
By now you probably know that omega-3s are a really good thing — they’re vital to keeping your mind and your body in working order. Fatty fish or a high-quality omega-3 supplement power your brain, protect your heart, and oil your joints.
When choosing a fish oil supplement, it can be daunting knowing which one is best. What’s the ideal dose of omega-3s? Should it be certified by a third party? And what’s the best source — fish or krill?
Read on to discover all you need to know about krill oil and omega-3s — and how to pick the best supplement for your needs.
Why take an omega-3 supplement?
Omega-3s are a type of essential fatty acid that are vital to fueling your brain, keeping you full, and more. Your body can’t produce these fats on its own — you have to get them from a supplement or from food. The best food sources are fatty fish, grass-fed beef, pastured egg yolks, and leafy greens.
There are different kinds of omega-3s:
- EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid): Both come from animal sources. Most fish oil supplements contain a combination of EPA and DHA, since they each carry benefits and complement each other.[ref url=”https://academic.oup.com/advances/article/3/1/1/4557081″][ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5003160/”] (more on their benefits below).
- ALA (alpha-linolenic acid): ALA comes mostly from plant sources. Humans can only convert up to 9% of ALA to DHA.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2621042/”] That’s why foods high in ALA like chia seeds and flaxseed oil aren’t high on the list of Bulletproof-approved foods. You’re better off getting your DHA directly from animal sources.
You also want to make sure you have the right ratio of omega-3s and omega-6s (another type of essential fatty acid), otherwise they end up competing for space in your body. The problem is, most Americans consume far too many omega-6s (mostly in the form of refined vegetable oils) and not nearly enough omega-3s. While omega-6s are beneficial in small amounts, too many cause inflammation in the body.
For most people, the ideal ratio is 1:1, although a 4:1 ratio (that’s 4 omega-6s for every 1 omega-3) might be a more realistic goal, since omega-6 is so abundant in the typical American diet. Most Americans eat a ratio that’s between 12:1 and 25:1, so you can see how skewed it is.
Since it’s not easy knowing whether you’ve got the balance right, taking an omega-3 supplement gives you peace of mind that you’ve covered your bases.
Learn more here about how to balance your omega-3 and omega-6 levels.
Krill oil vs. fish oil: Which one is best?
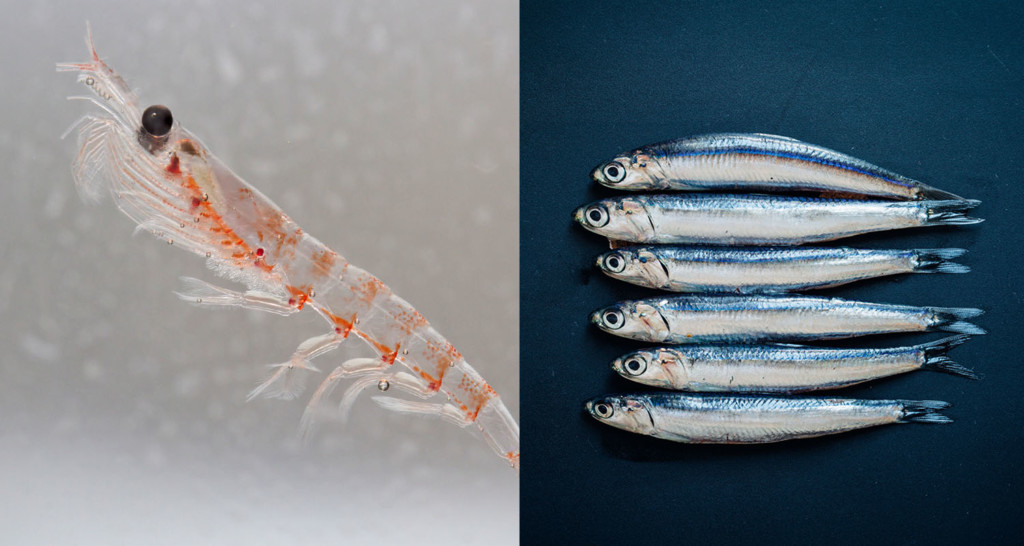

Krill oil comes from krill, tiny pink shrimp-like sea creatures. Fish oil is made from oily fish like sardines, herring, and tuna.
Fish and krill oil supplements both contain EPA and DHA, with one key difference: The omega-3s in krill oil are packaged as phospholipids, a type of fat. Phospholipids make up nearly every cell membrane in your body — that means you can absorb them quickly and easily.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21854650″][ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29222893″]
The EPA and DHA in fish oil are typically in the form of triglycerides — another type of fat molecule not as easily absorbed by the body.
So why not just take a krill oil on its own? Krill oil typically doesn’t contain a high enough dose of EPA and DHA to be majorly beneficial alone.
Which do you choose then — krill oil or fish oil? Ideally, both. Bulletproof Omega Krill Complex blends fish and krill oil together, so you get the high dose of EPA and DHA, coupled with maximum absorption.
Read on to find out what makes Omega Krill Complex different.
Benefits of Omega Krill Complex

Unique blend of Omega-3s

Omega Krill Complex combines wild fish oil, Antarctic krill oil, and Norwegian herring roe oil — the only supplement on the market to blend these three oils. Combining them increases their bioavailability and omega-3 levels. Like krill, herring roe also binds to phospholipids, making it easier for your body to absorb. It also has a DHA and EPA ratio of 3:1 — the same ratio found in human breastmilk.
High dose of EPA and DHA

Each serving (2 contains 885 mg of DHA and 480 mg of EPA — that’s way more than your average krill supplement, which has around 200 mg of DHA and EPA combined. Ditto for fish oil — typical supplements contain 500-1000 mg of DHA and EPA.
The higher the dose, the more likely you are to see benefits. In one study, 900 mg of DHA a day improved learning and memory in older adults.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20434961″]
Supports heart health
A high dose of EPA keeps triglyceride levels — the amount of fat in your blood — normal. In one study, men who took 1,350 mg of EPA a day had fewer triglycerides in their blood after 12 weeks.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16879829Paste the URL here”]
Strengthens your brain

There’s a reason why fatty fish and avocados are called “brain food”: Your brain is 60 percent fat, and it needs plenty of healthy fats to keep it running.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20329590″] DHA in particular creates and protects brain cells, keeps the brain’s electrical signals firing, improves memory, and protects brain cells from oxidative stress (when too many toxic molecules called free radicals damage your cells).[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29305120″][ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20088810″][ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21756134″] DHA is especially important for pregnant and breastfeeding women — it helps build and strengthen your baby’s brain. [ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21389181″][ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4728620/”]
Keeps skin supple and smooth
Each softgel contains 70 mg of gamma linolenic acid (GLA) from borage seed oil. GLA — an omega-6 fatty acid — hydrates and smoothes skin, and lessens acne.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24553997″][ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18761778″]
Fights free radicals
Omega Krill protects your body from free radicals with the help of two powerful antioxidants — astaxanthin and hydroxytyrosol.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21276280″] Astaxanthin is a bright red compound from algae, and hydroxytyrosol is a polyphenol found in olives.
Both antioxidants can also stop your LDL (aka “bad”) cholesterol from oxidizing, or getting damaged.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11521685″][ref url=”https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/2033″] Oxidized LDLs trigger inflammation and contribute to plaque buildup in the arteries, making your heart work harder.
Learn more here about the benefits of astaxanthin.
Tastes good

A common complaint about omega-3 supplements is the fishy aftertaste. Omega Krill solves that problem — flavored with oil from California lemons, it leaves you with a subtle citrus taste instead.
Sustainable

All of the fisheries that Bulletproof has partnered with are certified by the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC), the leading standards organization for wild-caught seafood[ref url=”https://www.msc.org/uk/media-centre/press-releases/msc-labelled-aker-biomarine-krill-products-are-from-a-sustainable-and-well-managed-fishery”], or Friends of the Sea, another international seafood certifying body.
RELATED: Krill Oil vs. Fish Oil: Battle of the Omega-3 Fats
How to use Omega Krill Complex

Each serving (2 softgels) contains 1,560 mg of omega-3s. Take two, twice a day, with food, and feel content knowing you’re taking one of the most powerful, high-quality omega-3 supplements on the market.