Free radicals are highly reactive molecules produced in the body naturally as a byproduct of metabolism (i.e., oxidation) or through exposure to environmental toxins such as ultraviolet light and tobacco smoke. Their instability stems from the fact that they contain at least one unpaired electron in their outer shell. Your body typically keeps a tight lid over the number of free radicals, but it occasionally loses control, resulting in a harmful situation in which a greater number of free radicals in the body can be kept in balance by antioxidants. To understand why this occurs, it is important to first recognize that electrons dislike being alone. In the case of free radicals, electrons constantly seek out another electron for themselves (which then stabilizes them). They do so by circulating in the body, pouncing on and binding to anything they encounter, including healthy cells, proteins, and DNA. This phenomenon is known as oxidative stress and can cause negative results on your body.
What causes an increase in free radicals?
Under normal circumstances, your body maintains a balance between free radicals and antioxidants – a state also referred to as “oxidative equilibrium”. Free radicals do not cause damage to your body so long as this oxidative stability is maintained. That said, two things could disrupt this delicate balance. The first is an increase in the production rate of free radicals, and the second is a decrease in the removal rate of free radicals.
The excessive production of free radicals and the resulting oxidative stress can be caused by several reasons. This might include:
- Lifestyle
- Diet
- Environmental conditions such as pollution and radiation
- Alcohol consumption and tobacco products
- Exposure to hazardous chemicals and pesticides
- Some medications
- Excessive physical exercise
Effects of excess free radicals on the body
Free radicals can damage DNA, predisposing them to breakage. Furthermore, it leads to the oxidation of lipids, which can harm various cellular components, including cell membranes. They can also oxidize individual amino acids, the building blocks of protein, by changing their structure and compromising the enzymatic function of proteins.
Oxidative stress can physically manifest as:
- Fatigue
- Muscle or joint pain
- Wrinkles and gray hair
- Headaches and sensitivity to noise
The harmful effects of oxidative damage on the body can sometimes be reduced with simple measures, such as by increasing your antioxidant intake.
Malondialdehyde
Malondialdehyde (MDA) is known as the end product of lipid peroxidation, a process in which free radicals attack fat molecules in the body. So, when you have increased levels of free radicals, you’ll have increased levels of MDA.
MDA reacts with DNA and proteins, causing cell damage and dysfunction. It also induces inflammatory responses and impairs immune function. In addition, MDA alters the structure and function of cell membranes, making cells more susceptible to damage and death. The accumulation of MDA in tissues is thought to be a major contributing factor to the aging process and several serious health conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, reducing the level of MDA in the body may help to prevent or delay the onset of age-related diseases.
Evaluation of MDA with Urine
The number of free radicals and the resulting level of oxidative damage present in the body can be determined by measuring MDA levels in urine. Put simply; you can use your MDA level as a rough indicator of the body’s current oxidative stress level. In general, the body is known to produce an excessive amount of free radicals due to factors like repeated exposure to an unpleasant environment, excessive exercise, overconsumption of food, and an inconsistent sleep pattern, among other factors. This underlines why you should pay attention to the concentration of MDA in your urine, as high levels of the MDA can indicate the need to tweak certain aspects of your daily lifestyle habits.
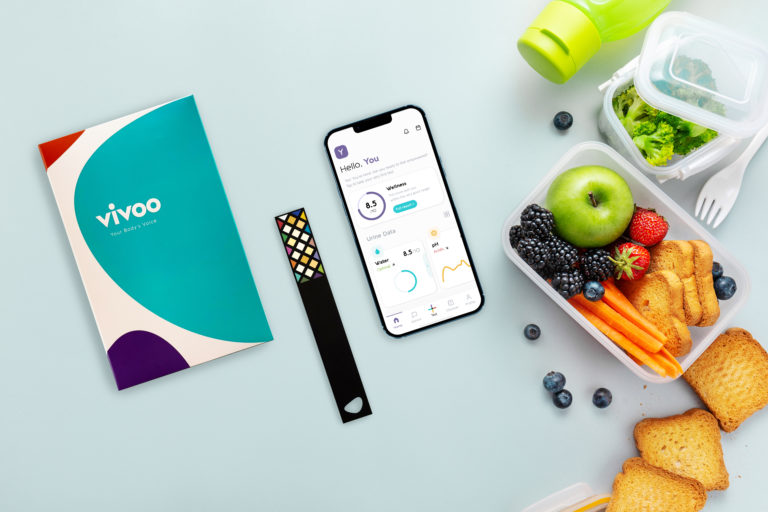
Getting real-time body data on MDA levels through urine as an indicator of oxidative stress is possible with at-home urine tests like Vivoo in the comfort of your home. It provides a low-cost and straightforward solution that does not require sophisticated equipment.
After urinating on the Vivoo test strip for a few seconds, the user scans the strip to the mobile application. Results are shared just in 90 seconds via the App no need to ship samples to a lab thanks to highly advanced image processing technology and artificial intelligence.
Try Vivoo now to get more insight into your oxidative stress level now with 30% OFF, use code DAVE30 at check out!
The Vivoo tests don’t just provide data on Oxidative stress but also on 9 parameters in total: Oxidative Stress, Vitamin C, Calcium, Magnesium, Hydration, pH, Ketones, Sodium and Proteins.
After taking the test, the user gets an overall wellness score and detailed feedback and scores on each parameter. The best part, the App then provides users with personalized nutritional and lifestyle advice to improve scores. All of the advice is prepared by dietitians, nutritionists and doctors.
It doesn’t end there; users can also sync their wearables to gain insight into sleep, activity, and heart rate. Also, read wellness articles on trendy topics and order personalized supplements according to their Vivoo test results.