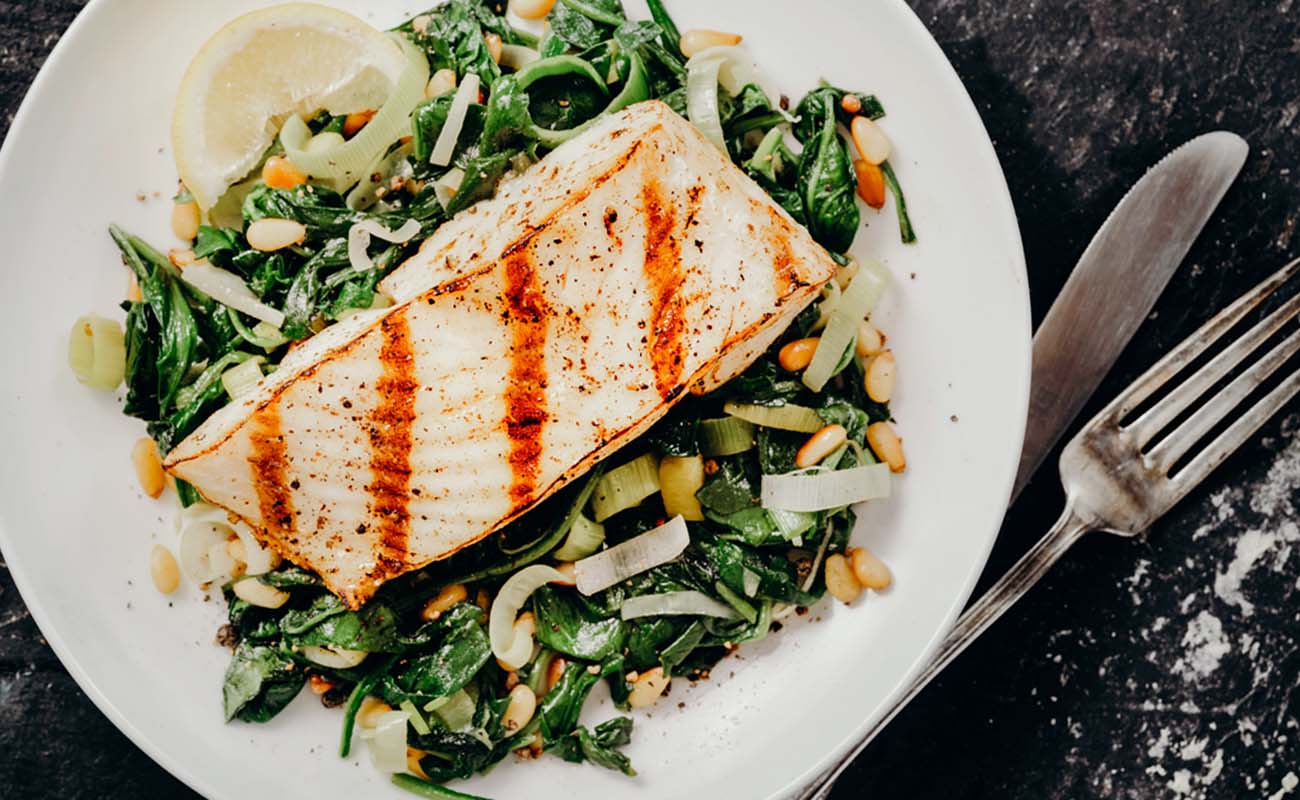
- Can you reverse diabetes? It depends on type, stage, and several other factors, many of which are totally in your control.
- Diabetes symptoms include things like increased hunger, increased thirst, frequent urination, slow wound healing, and blurred vision, to name a few.
- Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects an estimated 23.1 million people in the US, and as many as 1 in 4 people don’t know they have it. That doesn’t count people who are prediabetic or at risk for developing diabetes.
- When insulin is working well, your cells get the energy you need and you don’t store excess fat. A couple things can go wrong with this process, though.
- Read on to find out what diet and lifestyle changes can keep your blood sugar level and regulate your insulin production.
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects an estimated 23.1 million people in the U.S., and as many as 1 in 4 people don’t know they have it.[ref url=”https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pdfs/data/statistics/national-diabetes-statistics-report.pdf “] Numbers have steadily climbed over the past few decades with no signs of leveling off. Diabetes symptoms include things like increased hunger, increased thirst, frequent urination, slow wound healing, and blurred vision, to name a few.
All doctors approach diabetes differently, and the management of it depends on whether your doctor focuses on prescriptions or takes a more holistic approach. Some doctors will decide whether or not you need insulin medication, and how much. Others will advise you on diet and lifestyle changes that can help.
Diabetes is one of those conditions where conversations with your doctor will be much more productive if you have some information about what’s going on. Read on to learn the basics about how diabetes and insulin work, and how to improve your condition whether you’re at risk or if you already have diabetes.
Type I vs. type II diabetes
As of now, diabetes is classified as either Type I or Type II. New research suggests there are several more types of diabetes, which all require different treatment approaches, but that’s a developing area of knowledge. On an episode of Bulletproof Radio, Dr. Steven Masley explains why doctors are starting to view Altzheimer’s disease as “type III diabetes” and picks apart the relationship between insulin and brain degeneration. Listen to it on iTunes.
With Type I diabetes, your immune system attacks the pancreas, and it makes less and less insulin over time. With Type II diabetes, your cells become insulin resistant (more on that coming up), and your pancreas struggles to keep up with the demand for even more insulin.
Type I diabetes is tricky because of the autoimmune component. Keeping inflammation low quiets your immune system so you can preserve the insulin-producing beta cells in your pancreas that you still have.
Type II diabetes is more responsive to diet and lifestyle changes, and countless people have had success reversing their diabetes by taking control of their diet and life.
Whether you have Type I diabetes, Type II diabetes, prediabetes, or if you can feel blood sugar fluctuations around your eating patterns, you’ll benefit from diet and lifestyle changes that benefit your blood sugar.
How insulin works
Before you get too deep, first understand how insulin plays into it all.
When you eat something, your body breaks food down into amino acids (protein), lipids (fats), and glucose (sugar). Sugar goes into your bloodstream for delivery to your cells to give them the fuel they need to do their jobs.
Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get where it needs to go. When your body senses that you’ve eaten something, your pancreas produces insulin to help your cells absorb sugar. If you didn’t have insulin, your cells wouldn’t receive their glucose fuel, and your body would sense sugar in your bloodstream and eventually store it as fat because your cells didn’t use it.
When it’s working well, your cells get the energy they need and you don’t store excess fat. A couple things can go wrong with this process, though.
Insulin resistance is exactly as it sounds — your cells don’t get the signal from insulin to absorb sugar. If your muscle and organ cells do not respond to insulin and absorb blood sugar, your cells don’t get the fuel they need and sugar stays in the bloodstream. That signals your body to store it as fat.
If your cells aren’t responding to insulin, your pancreas produces more to turn up the volume on the signal that glucose is available and the cells should absorb it. When your pancreas can keep up, blood glucose stays within healthy ranges, and all is well. When your pancreas starts to poop out, you end up with insulin deficiency, which leads to blood sugar fluctuations and weight gain.
Insulin resistance demands more insulin from your pancreas. Pre-diabetes is when you don’t make quite enough and your blood sugar levels rise, but they’re not yet high enough for an official diabetes diagnosis.
Our job is to make food and lifestyle choices that will keep that process humming. Here are some research-backed things you can incorporate to get a handle on insulin resistance, prediabetes, and diabetes.
If you do nothing else, cut sugar

Piles and piles of research link high sugar consumption with diabetes.[ref url=”https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0031938410000600 “][ref url=”http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/33/11/2477.short “][ref url=”https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/199317?version=meter%20at%20null&module=meter-Links&pgtype=Blogs&contentId=&mediaId=%%ADID%%&referrer=&priority=true&action=click&contentCollection=meter-links-clickPer “][ref url=”http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/26/4/1008.short “] That’s because nature doesn’t make the super sugary foods and drinks that humans manufacture, and we aren’t built to handle it.
Your body breaks down the food you eat into sugar (glucose) that your cells can use for fuel. Humans are built to handle blood sugar levels that come from meals of meats and vegetables with a moderate amount of fruits.
In the last few hundred years or so, people started to isolate sugar into an ingredient and sweeten foods with it (maple syrup, high-fructose corn syrup, and other sweeteners included).
Sugary foods cause a spike in the glucose in your blood. Your body can handle the occasional surge, but when sweets become an everyday thing, your body starts to struggle to deal with it. The overwork tires out your pancreas, and produces less and less insulin, which keeps glucose in your blood instead of in your cells where it belongs.
Especially in the early stages of insulin resistance, prediabetes, and diabetes, simply cutting sugar drastically reduces your insulin demand, and in turn reduces the burden on your pancreas.
The most detrimental thing sugar does is cause inflammation, and inflammation is the root of almost everything that misfires in your body. There is a direct link between inflammation and diabetes,[ref url=”http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S000291490502028X”] and a lower carb diet reduces C-reactive protein, a marker of inflammation.[ref url=”http://jn.nutrition.org/content/142/2/369.short “] In addition to sugar, it’s a good idea to keep an eye on your toxic load and keep your omega-3 to omega-6 ratio low to keep inflammation down.
Lose weight

Although scientists do not yet understand the exact causes of insulin resistance, excess body weight is on the suspect list.
Researchers found that participants with diabetes went into remission by losing weight alone — even without taking insulin.[ref url=”http://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(17)33102-1/fulltext?elsca1=tlpr”]
If you’re not yet diabetic but you’re at risk, or if you can feel your blood sugar fluctuations (crashing and needing to eat, or feeling “hangry”), consider losing weight to reduce your risk. In one study, for every kilogram of weight loss (a little over 2 lbs), there was a 16% reduction in risk.[ref url=”http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/29/9/2102.short”]
Another study followed adults at high risk for diabetes for 10 years and found that people who made diet and lifestyle changes had a lower incidence of diabetes than participants who got metformin (a medication to control blood sugar) or placebo.[ref url=”https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0140673609614574#!”]
If you’re overweight, chances are you’re at risk for diabetes or you’re already there. It might be time to start looking into changing the way you eat.
Which brings us to…
The ultimate diabetes diet: go keto

The research is so solid that the medical community is catching on and starting to advise diabetic patients to limit carbs.[ref url=”http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0002934387900581″] Study after study shows that a high-fat, low-carb, ketogenic diet reverses Type 2 diabetes.[ref url=”https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11010-007-9448-z “][ref url=”http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0899900712000731″]
If your carb consumption is on the high side (once you add sugar into the mix, you’re most certainly on the high side), it’s stored as fat and you end up with insulin resistance or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.[ref url=”http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1043276010001712″] The reason behind it is that carbs metabolize into glucose, and limiting carbs helps your body control blood sugar more efficiently.[ref url=”https://nutritionandmetabolism.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1743-7075-5-36?wptouch_preview_theme=enabled”][ref url=”https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/52/3/524/4650824″] It improves overall blood sugar profiles, insulin sensitivity, and hemoglobin A1c, which is a diabetes marker.[ref url=”http://annals.org/aim/article-abstract/718265/effect-low-carbohydrate-diet-appetite-blood-glucose-levels-insulin-resistance”] Going low-carb is especially effective if you’re in the early stages when you do not yet need to administer insulin.[ref url=”https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/002604959290111M”]
Reducing carbs and upping your intake of high-quality fats reduces fat in your blood,[ref url=”http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/nejm198809293191304″] which in turn lowers your risk of diabetes.
Even if making small gradual changes over time doesn’t cure you, you’ll feel so much better when you give your body what it needs and when you don’t burden it with what it doesn’t need. Whether you’re reducing your risk of developing diabetes or eliminating your need for medication, it’s worth incorporating worthwhile changes so you can be the best version of yourself.