If you’re a pet owner, then you know that cuddling with your dog or cat gives you all the feels. It can also lower stress, according to a new study published by the American Educational Research Association.
Researchers at Washington State University found that petting and playing with a dog or cat for just 10 minutes significantly lowered cortisol (the stress hormone).
As part of the study, 249 college students were divided into four groups. The first group got to interact directly with dogs and cats for 10 minutes. The second group got to observe others petting the animals, while the third group watched a slideshow of the same animals. The fourth group was “waitlisted” and told to wait quietly for their turn.
The researchers collected a number of salivary samples from each student, starting in the morning when they woke up. The students who had direct contact with the dogs and cats showed significantly less cortisol in their saliva after the interaction.
“We already knew that students enjoy interacting with animals, and that it helps them experience more positive emotions,” says lead author Patricia Pendry, an associate professor in WSU’s Department of Human Development. “What we wanted to learn was whether this exposure would help students reduce their stress in a less subjective way. And it did, which is exciting because the reduction of stress hormones may, over time, have significant benefits for physical and mental health.”
Pendry and her team are conducting further research, looking at the impact of a four-week-long animal-assisted stress prevention program.
If you’re looking for other ways to ease stress, check out this definitive guide to stress management.
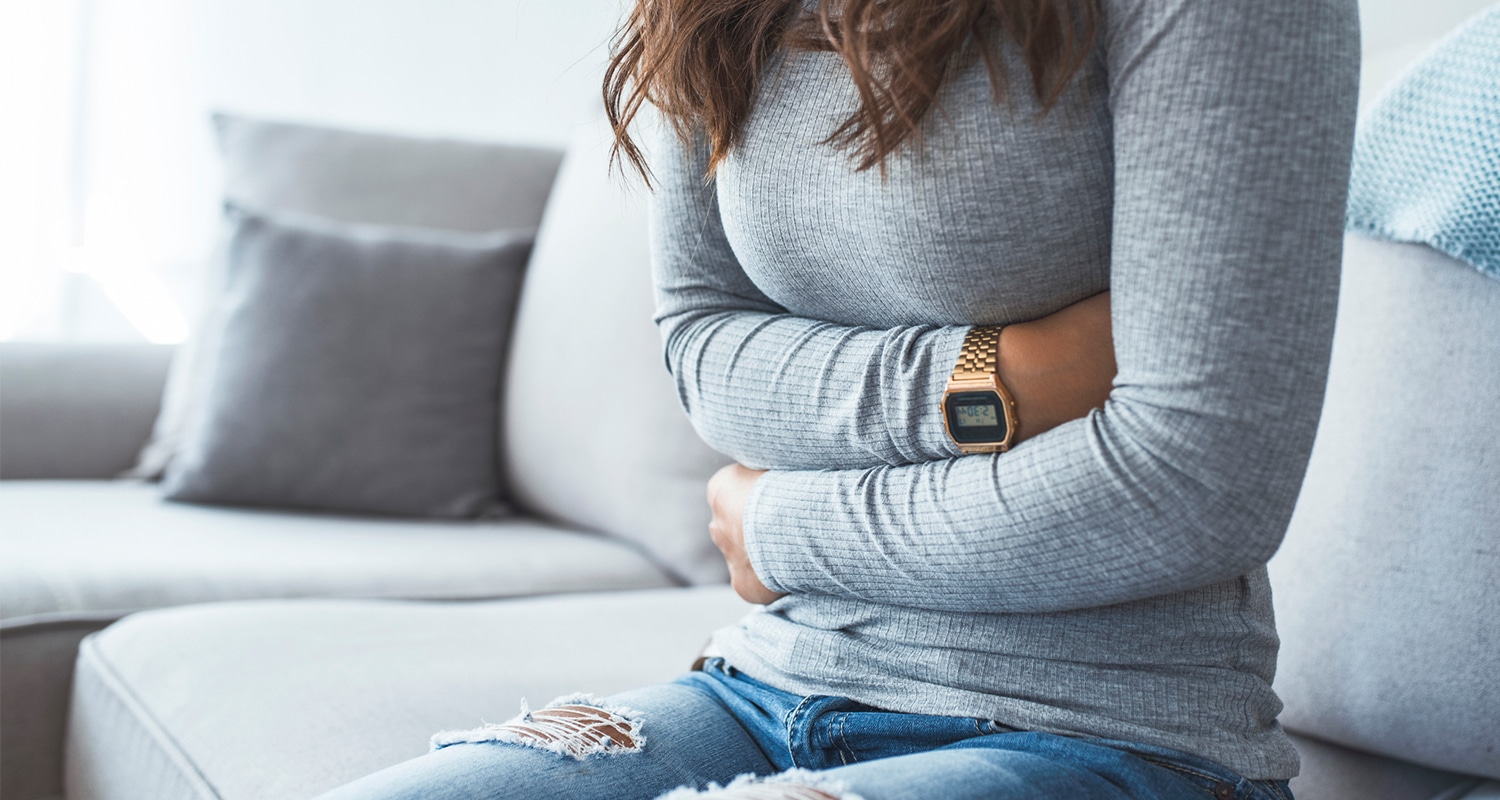 Heartburn, indigestion, and acid reflux all refer to the same thing – the burning feeling you get when acid from your stomach comes up into your esophagus. “Up” is the wrong direction for digestive fluids, for the record.
Heartburn, indigestion, and acid reflux all refer to the same thing – the burning feeling you get when acid from your stomach comes up into your esophagus. “Up” is the wrong direction for digestive fluids, for the record. Many medical doctors will tell you that if you’re feeling the burn, you have too much stomach acid and you need over-the-counter antacids or prescription acid blockers.
Many medical doctors will tell you that if you’re feeling the burn, you have too much stomach acid and you need over-the-counter antacids or prescription acid blockers.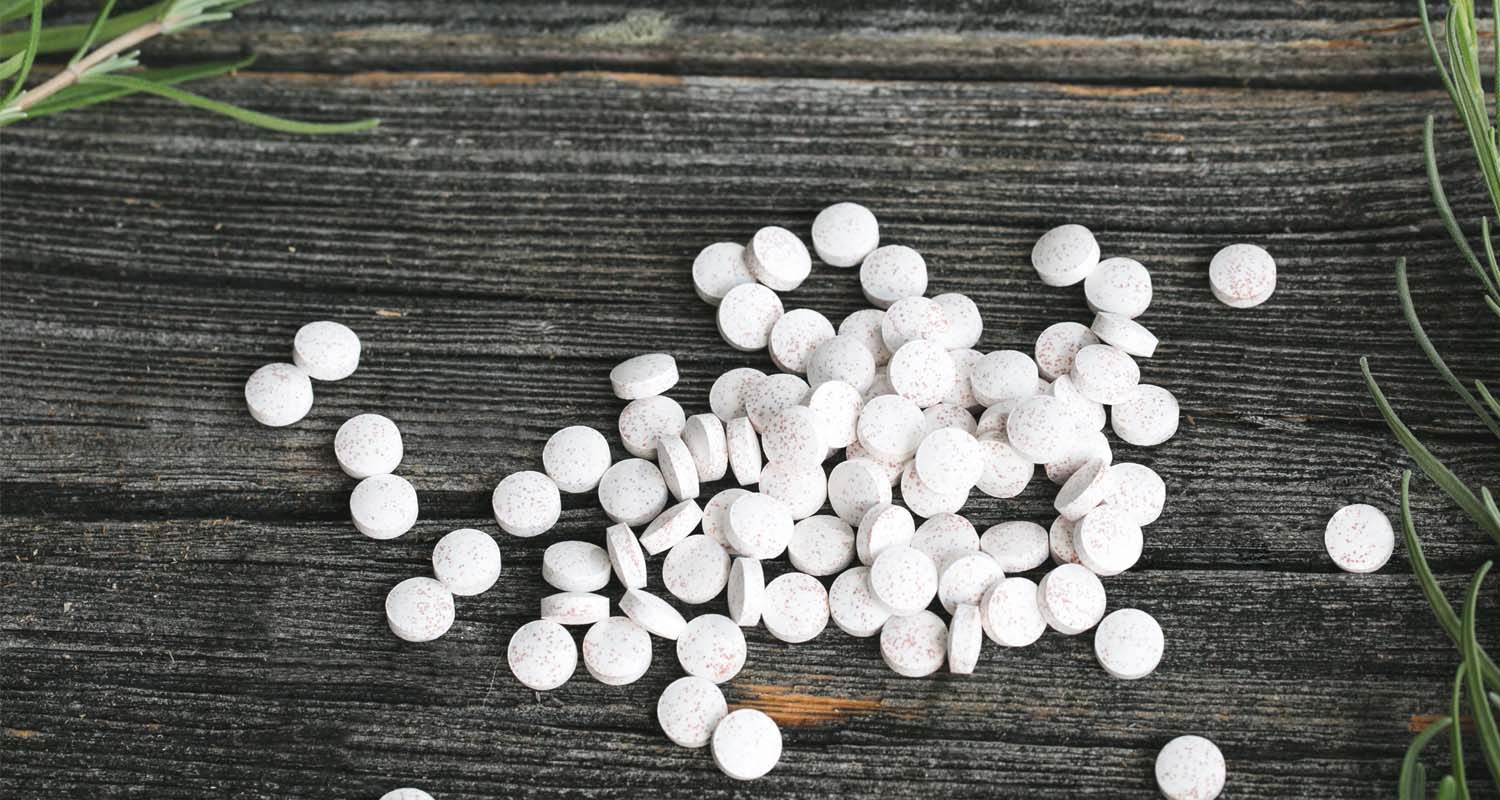  It seems logical that if you feel burning, there must be way too much acid that’s causing the feeling your esophagus. Turns out, most acid reflux is not from
It seems logical that if you feel burning, there must be way too much acid that’s causing the feeling your esophagus. Turns out, most acid reflux is not from This isn’t a replacement for a real diagnosis, but the burp test can give you an idea of what you’re working with. Do this first thing in the morning, before eating or drinking anything.
This isn’t a replacement for a real diagnosis, but the burp test can give you an idea of what you’re working with. Do this first thing in the morning, before eating or drinking anything. Modern medicine is amazing, and
Modern medicine is amazing, and  It’s counterintuitive, but you might need to increase your stomach acid.
It’s counterintuitive, but you might need to increase your stomach acid.  Your stomach produces hydrochloric acid naturally, and betaine HCL tablets fill the gap if you’re not producing enough.
Your stomach produces hydrochloric acid naturally, and betaine HCL tablets fill the gap if you’re not producing enough.  Unlike powdered rhinoceros horn, dried tiger penis, and most other traditional aphrodisiacs, maca actually seems to work. There’s some evidence to back up claims of its sex-enhancing properties. Here’s what the science says about maca.
Unlike powdered rhinoceros horn, dried tiger penis, and most other traditional aphrodisiacs, maca actually seems to work. There’s some evidence to back up claims of its sex-enhancing properties. Here’s what the science says about maca. In a double-blind 2002 study, researchers gave 57 men either 1.5g maca, 3g maca, or placebo. The men received the supplements daily for 12 weeks. After 8 weeks, men in the two maca groups reported heightened sexual desire.[ref url=”http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12472620″]
In a double-blind 2002 study, researchers gave 57 men either 1.5g maca, 3g maca, or placebo. The men received the supplements daily for 12 weeks. After 8 weeks, men in the two maca groups reported heightened sexual desire.[ref url=”http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12472620″]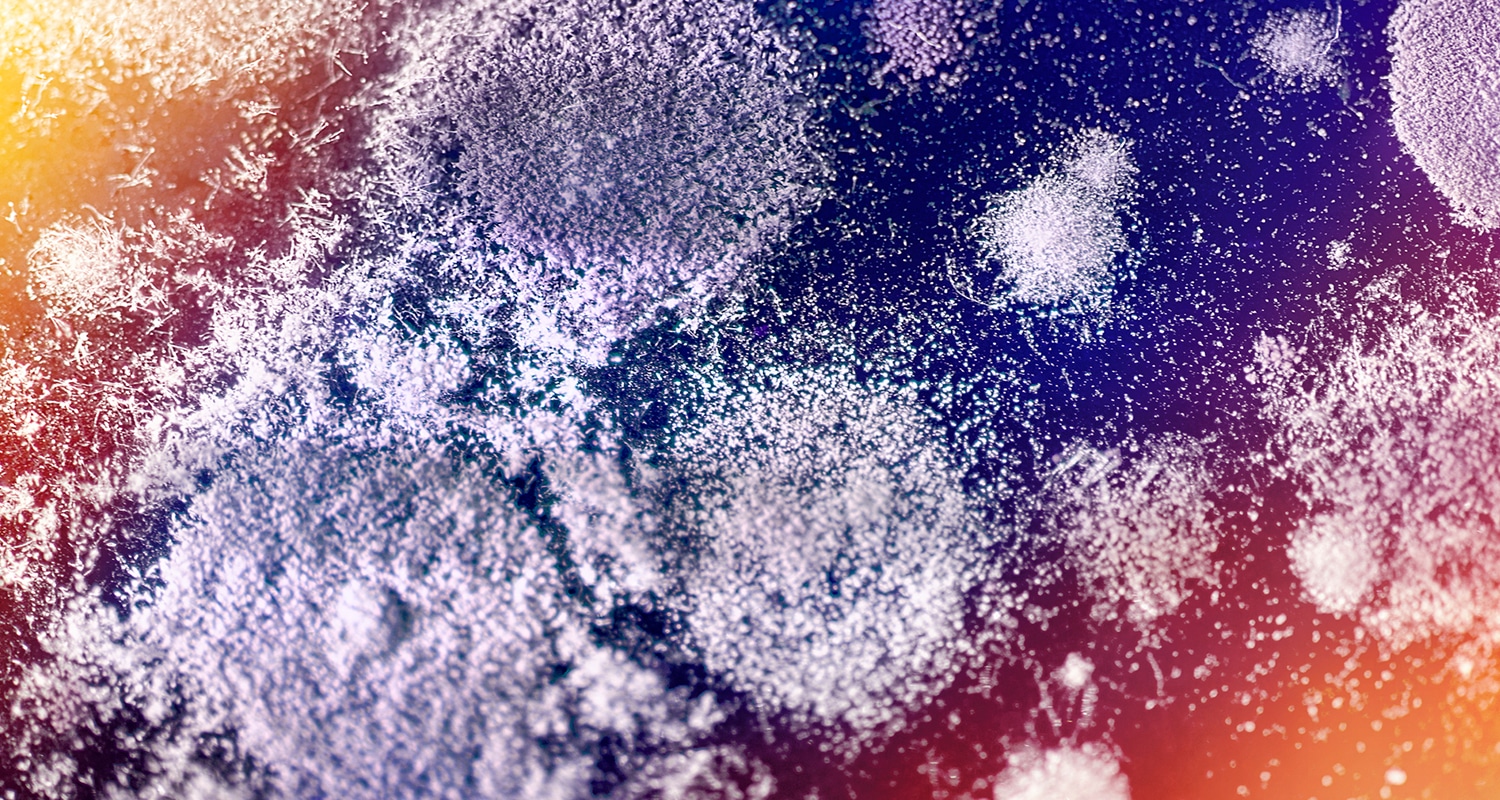 Maca root gets moldy. Traditionally, Peruvians dry maca root and crush it into a powder. Dried maca powder is what you’ll typically find in health food stores as well. The trouble is that maca often grows mold during the drying process, and the resulting powder often contains aflatoxin, a potent carcinogen. Maca was on the drawing board as a Bulletproof product for a while, but it was difficult to find a pure source; even the highest quality maca root contained about 13 ppb aflatoxin. That’s not up to Bulletproof standards.
Maca root gets moldy. Traditionally, Peruvians dry maca root and crush it into a powder. Dried maca powder is what you’ll typically find in health food stores as well. The trouble is that maca often grows mold during the drying process, and the resulting powder often contains aflatoxin, a potent carcinogen. Maca was on the drawing board as a Bulletproof product for a while, but it was difficult to find a pure source; even the highest quality maca root contained about 13 ppb aflatoxin. That’s not up to Bulletproof standards. While maca looks and tastes like a root, it’s actually a cruciferous vegetable, which is the same category as cauliflower, kale, cabbage, Brussels sprouts, and other members of the Brassica family. And like other cruciferous veggies, maca contains goitrogens, anti-nutrients that disrupt thyroid hormones. There are two ways to reduce goitrogens in maca root.
While maca looks and tastes like a root, it’s actually a cruciferous vegetable, which is the same category as cauliflower, kale, cabbage, Brussels sprouts, and other members of the Brassica family. And like other cruciferous veggies, maca contains goitrogens, anti-nutrients that disrupt thyroid hormones. There are two ways to reduce goitrogens in maca root. Maca has a malty, nutty, slightly sweet flavor that pairs well with chocolate and vanilla, so it’s a great addition to smoothies or protein shakes. You could even spoon some into your morning coffee, although the high starch content may take you out of ketosis. However you take it, be sure your maca’s cooked, and get the high-quality stuff to avoid mold toxins as much as possible.
Maca has a malty, nutty, slightly sweet flavor that pairs well with chocolate and vanilla, so it’s a great addition to smoothies or protein shakes. You could even spoon some into your morning coffee, although the high starch content may take you out of ketosis. However you take it, be sure your maca’s cooked, and get the high-quality stuff to avoid mold toxins as much as possible.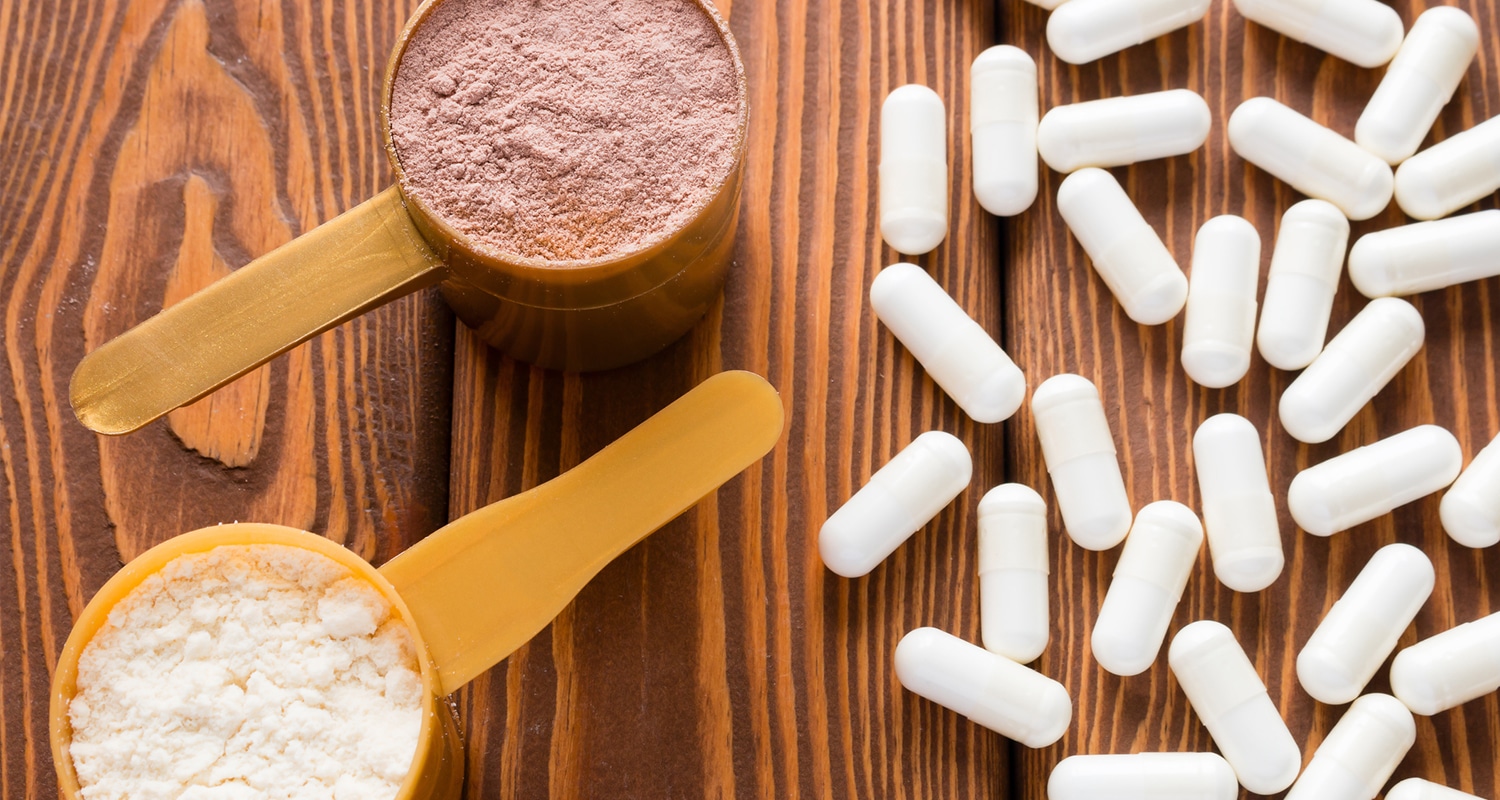 To use maca powder, mix one teaspoon, which is roughly 5g, into your smoothie or protein shake.
To use maca powder, mix one teaspoon, which is roughly 5g, into your smoothie or protein shake.