[tldr]
- Music industry mogul Rick Rubin is the co-founder of Def Jams Recordings and renowned producer of household names like the Beastie Boys, Adele, Johnny Cash, Led Zeppelin, Justin Timberlake, and the list goes on.
- Rubin recently chatted with Bulletproof founder and CEO Dave Asprey about his favorite biohacks to think clearly and maximize his creativity.
- Keep reading to find out what Rubin does to stay on top of his game, as well as one big health challenge he’s faced along the way.
[/tldr]
Music industry mogul Rick Rubin is the co-founder of Def Jams Recordings and a renowned producer of household names like the Beastie Boys, Adele, Johnny Cash, Led Zeppelin, Justin Timberlake, and the list goes on. (And on, and on.)
In a recent Bulletproof Radio podcast episode (iTunes), Rubin chatted with Bulletproof founder and CEO Dave Asprey about his favorite biohacks to think clearly and maximize his creativity. Keep reading to find out what Rubin does to stay on top of his game, as well as one big health challenge he’s faced along the way.
A good night’s sleep is essential to creativity. Instantly download the Bulletproof Sleep Roadmap to feel refreshed and ready every morning.
Rick Rubin’s top 9 biohacks
1. Get distracted

Rubin suggests swimming, drawing, walking, or going for a drive as ways to distract yourself with intention. The best part of distraction? You can do whatever you want as long as it shifts your focus. Plus, it’s free!
2. Meditation for focus and patience

“[Meditation] develops your ability to focus in a deep way, in a deep and patient way,” says Rubin.
Rubin has several different types of meditation styles in his toolbox, each for different scenarios: Transcendental Meditation® for mornings, guided meditations for when he’s feeling down, and loving-kindness (aka metta) meditation during exercise or walking, among others.
He weaves meditation throughout his day, and it doesn’t always have to be a big production with a designated place and time. “I think any opportunity to meditate is good,” says Rubin. “There’s no bad version, it’s never too short, and it’s never too easy. If you decide to do a three breath meditation, it’s great.”
Related: 30-Day Meditation Challenge for Beginners (With Guided Meditations)
3. Cryotherapy
Ready to try an ice bath? Here’s how to do it:
- Fill your tub or a kiddie pool halfway with cool water.
Add a bag of ice (from the grocery store or gas station). - Get in slowly, submerging just your lower half at first.
- Stay in for a minimum of three minutes. You can take a break if you need to, but aim for three minutes total. As you repeat the practice, you can go longer and longer each time, working your way up to 15 minutes.
IMPORTANT: Make sure someone else is at home to check on you, especially if you’re just starting out with ice baths. Your body can go into shock if you submerge your whole body or if you stay in too long, especially when you’re first starting out. Also, if you have Raynaud’s disease (where your blood vessels constrict from cold), problems with circulation, or if you’re hypothyroid and do not tolerate cold, you can get the same benefits with a cold shower or an ice face bath.
Cryotherapy does so much more than just help you be in the present moment. Read this article for more benefits of cryotherapy.
Related: Cryotherapy for Better Skin and Hair
4. Let go of dogma and admit when something’s not working

He sought out the medical advice of experts far and wide, including a highly respected Tibetan doctor who told him to start with bone broth. But he refused to drink it, because he was a “brainwashed vegan,” as he puts it.
He eventually started slowly adding animal protein like eggs and fish into his diet, which was the starting point to getting his health back on track. Once he changed his diet and got his sleep-wake cycles back to a healthy rhythm with the help of Dr. Phil Maffetone, an expert in human performance with a background in Chinese medicine, the weight started to come off.
It can be difficult to change your own mind once you’ve developed strong opinions about something, he adds “I feel bad because as a vegan, I was preaching veganism. It comes with the territory,” says Rubin. But being open to a new lifestyle literally saved Rubin’s life.
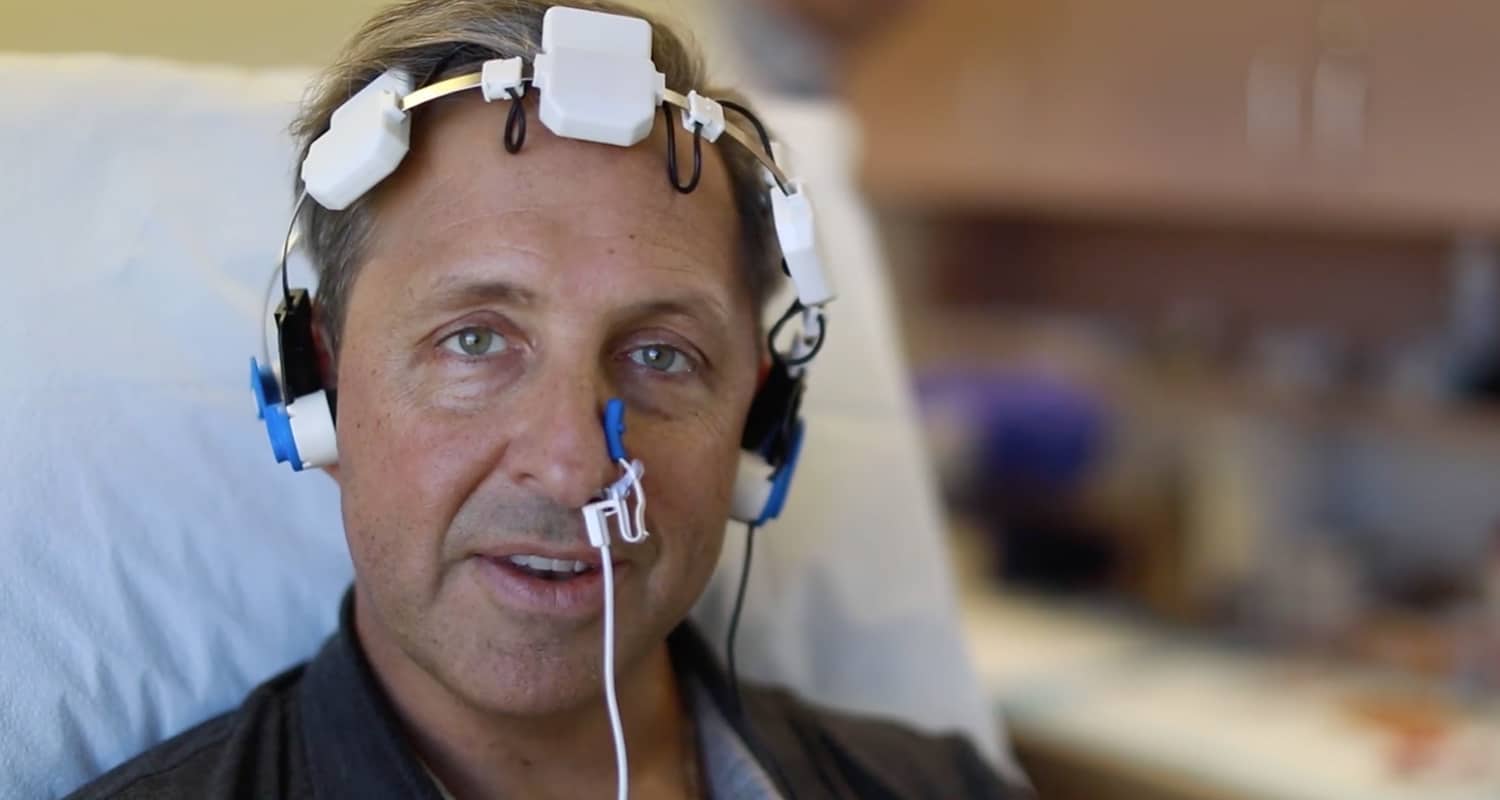
5. Cranial Electrical Stimulation (CES)

Related: How to Boost Your Alpha Brain Waves to Lower Stress and Improve Mood
6. Red light
- Increased energy
- Improved sleep
- Clearer thinking
- More stable moods
- Reduced headaches
- Improved immunity
He also wears blue-blocking glasses every evening, and has only red lights in his home. He also has a Sauna Space tent in his home which combines the detox benefits of infrared sauna with the benefits of red light, all in one.
7. Carbogen
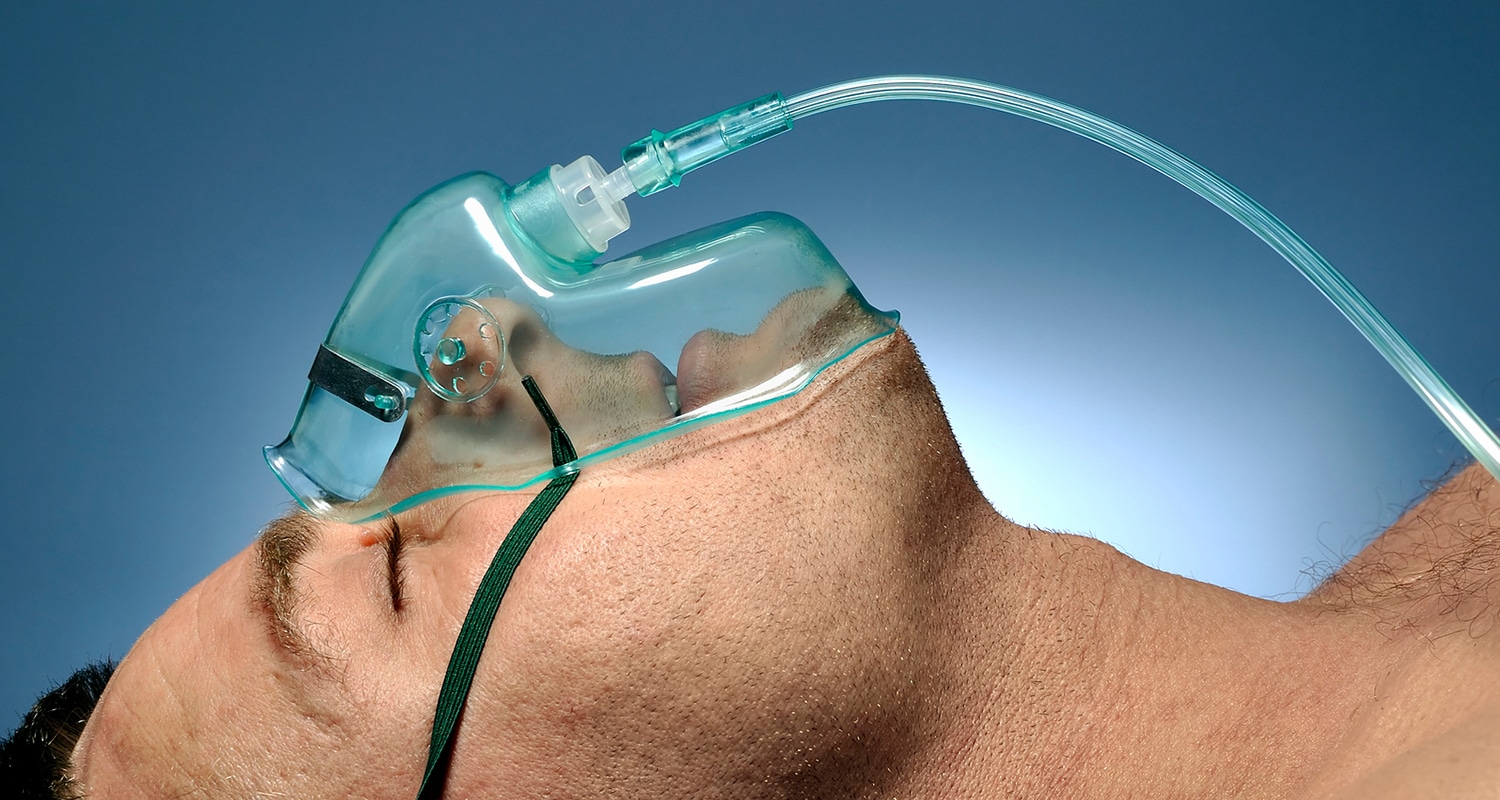
You can do this at clinics that offer carbogen therapy, or you can drop a couple thousand on a carbogen generator for your home. Rubin has also experimented with hyperbaric oxygen.
8. OURA Ring

9. Prayer

To amp up your creativity, try one or two of Rick Rubin’s favorite biohacks at a time, and see if you notice a difference in your creative work. Does your muse come more easily? Do you slip into the flow state more readily than you did before? Every creative professional and hobbyist has his or her favorite routines that get the juices flowing. It’s up to you to find yours.
















