by Dave Asprey
by Team Asprey
This is Part 2 of the Are Humans Vegans or Omnivores mini-series by guest author Nora Gedgaudas, CNS, NTP, BCHN, an internationally acclaimed keto and ancestral nutrition specialist. You can read Part 1 of the mini-series here, and hear her chat live with Dave at PaleoFX on this episode of Bulletproof Radio (iTunes).

That calm center was the clarity that came from better understanding of how we evolved as a species and what the forces were that actually shaped our physiological makeup and nutritional requirements in the first place. From that moment forward, all confusion ceased and led to a deeper and more rational curiosity about our human origins and that, which served to make us human.
My primary curiosity centered around the question: Did we actually evolve as and from an herbivorous primate species?
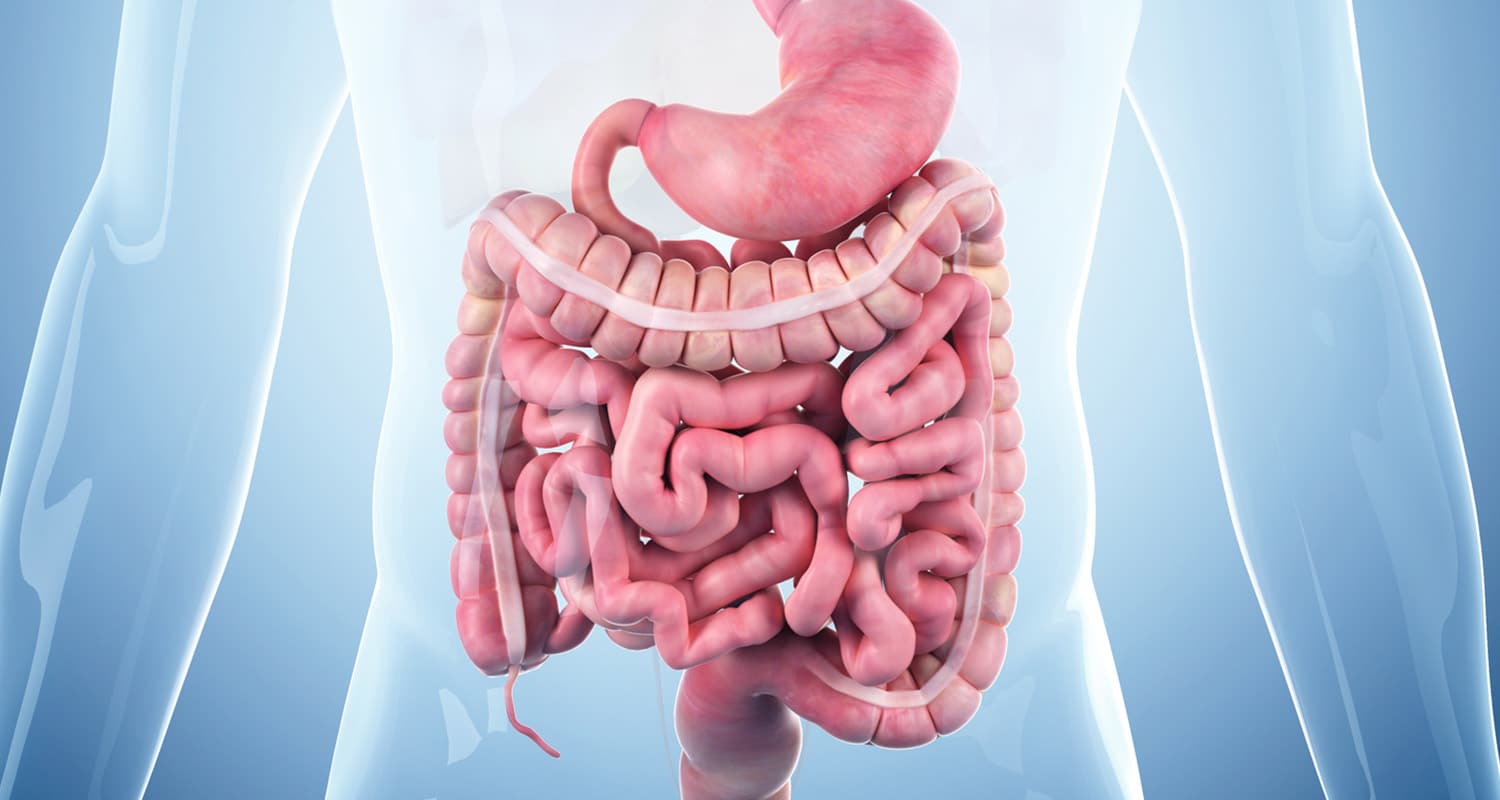
In contrast, the fermentative portion of the human digestive tract occupies only about half of what would be expected of a primate of our size and is no more than 20% of its total capacity. Most nutrients synthesized by our gut bacteria are slated for themselves, and not us. While well-fed gut bacteria benefit our immune system, sleep quality, appetite, and more, we lack the ability to fully extract the full spectrum of nutrients from plant foods that herbivores are able to extract.
The digestive systems of pure herbivores are simply different from ours. One extreme example, ruminants like cows and sheep, have four stomachs that help them synthesize every nutrient they need from grass and weeds alone.
RELATED: Eating Meat Doesn’t Harm the Environment as Much as You Think
We instead rely on the extraction of nutrients from the animals we consume. They have already synthesized many of our essential and most beneficial nutritional compounds — many of which are entirely unique to animal foods. Examples include fully formed fat-soluble nutrients like true vitamin A (retinol), vitamins D3 and K2 (MK-4), conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) and long-chain fatty acids such as EPA/DHA, along with CoQ10, carnitine, and B12.
We even developed the ability to absorb heme-based iron, found exclusively within the blood, meat and organs of animals. Herbivores are incapable of metabolizing heme-based iron,[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6763339″] and humans do not as efficiently absorb non-heme iron. In effect, our human digestive system much more closely resembles that of a carnivore than any herbivore.
If you don’t mind a little geeky terminology thrown in here, it is revealing to pay attention to the language used by the authors of this important study:
“Unique among extant primates, modern humans are anatomically adapted to regularly consume substantial amounts of vertebrate animal tissues (meat, organs, etc.). Over the last several million years, the hominin gastrointestinal tract has evolved from a chimpanzee-like large-intestine-dominated configuration well adapted for digesting fruits and other plant parts (as well as the occasional small mammal) to a more carnivore-like small-intestine-dominated form well suited for extracting complex nutrients from animal remains.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3329511/”][ref url=”Kaplan H, Hill K, Lancaster J, Hurtado M (2000) A theory of human life history evolution: diet, intelligence, and longevity. Evol Anthropol 9: 156–185 doi: 10.1002/1520–6505 (2000).”] Increased consumption of animal tissues likely fueled brain expansion in the genus Homo[ref url=”https://www.scholars.northwestern.edu/en/publications/effects-of-brain-evolution-on-human-nutrition-and-metabolism”][ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28524347″][ref url=”https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0047248489900353″][ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21452485″] and may have helped to facilitate initial hominin dispersals out of Africa.”[ref url=”https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0047248402906020″]
The fact that we are technically termed “omnivores” does not by definition automatically imply that we are able to successfully derive 100% of our critical nutrition from either plant or animal foods equally. Our very physiological design clearly indicates that animal products are an integral part of human health.

Whatever plants early humans would have consumed along the way would have been wild, largely fibrous and uncultivated. We would have eaten plant tubers uncooked, which would not have been digestible. In their raw form, the starch in roots and tubers isn’t absorbed in the small intestine and it passes through the body as non-digestible carbohydrate. Heating breaks down the cell walls and makes starch much more accessible to breakdown by digestive enzymes. Regardless of whether fire for thoroughly cooking starch-based foods was available to us or not, we would not have eaten meaningful amounts of starchy tubers early on in any case.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2981409″][ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16441938″]
Also, even when thoroughly cooked, roots and tubers are only able to provide an estimated 1,882 kJ/hour to 6,120 kJ/hour (almost pure starch), versus the estimated 63,398 that large, fat-rich game provides.[ref url=”http://www.evolbiol.ru/docs/docs/large_files/hominin_diets.pdf”] Meat and fat are far more efficient energy sources.
This does not even take into account the relatively far poorer nutrient content and non-existent essential fatty acid content (and non-available fat, in general) of roots and tubers. The time and laborious energy versus caloric and nutrient return required to procure, prepare, and digest such foods would also have made them anything but preferable under normal circumstances where game was readily available.
Also, early humans’ enormous consumption of meat alone would likely not have left a lot of room for that baked potato alongside our wooly mammoth steaks. Starch would really never have been an especially meaningful source of calories, save under the direst of circumstances (assuming the capacity of fire production-at-will was even available).
We would have also been limited in our (even now, highly variable) capacity to even digest fully cooked starch by limitations in our capacity for amylase production (a starch digesting enzyme). Our chimp cousins carry only two rudimentary copies of amylase genes needed to digest starchy foods. Research reports that our species likely only experienced an increase in copies of amylase genes within the last 200,000 years, and we already had our big brains by then.[ref url=”http://www.evolbiol.ru/docs/docs/large_files/hominin_diets.pdf”]
Today, humans vary in their amylase-digesting capacity rather widely, and most have a range of anywhere from two copies up to 16 copies of amylase genes, making starchy carbs (yet again) anything but essential to our health as a species. According to the above-referenced study (Perry GH, et al) the adaptation to significant starch consumption was likely not within our capacity during the Middle Pleistocene and is not even present in many low starch consuming populations today.

Even as we continued to consume plant foods along the way over the course of our evolution, it is plainly obvious that these were a secondary food source for early humans, at best (think: side dish).[ref url=”https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229092582_FOCUS_Gough’s_Cave_and_Sun_Hole_Cave_Human_Stable_Isotope_Values_Indicate_a_High_Animal_Protein_Diet_in_the_British_Upper_Palaeolithic”][ref url=”https://www.springer.com/us/book/9781441967329″][ref url=”https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0028689″] Vegetables were also a food having a far greater cost-to-benefit ratio on multiple levels, also taking into account the relative potential toxicity of wild plants and their comparatively poor digestibility, nutrient availability and caloric value — even cooked.
It is easy to demonstrate and reasonably conclude that our species was never, ever even close to being vegetarian, much less vegan. Vegetarianism and especially veganism is a purely modern-day experimental invention not even shared by our most distant primate cousins. We traded big guts for big brains, instead. I personally like to think that was a good tradeoff.
by Dave Asprey
by Dave Asprey
[tldr]
[/tldr]
In a recent study, scientists made the connection between specific strains in the gut bacteria of rats, and their mood and behavior.[ref url=”https://www.nature.com/articles/s41380-019-0380-x”]
Rats were split into two groups — one group got to chill in a relaxed environment, and the others were grouped with aggressive rats to rile them up. Within the high conflict group, rats were categorized as resilient or vulnerable, depending on how quickly they backed down to the aggressive rats. After a few days of frequent conflicts, researchers analyzed the gut bacteria profile of fecal samples of both groups.
Researchers found that vulnerable rats had more Actinobacterium, Bacillus, and Clostridium strains and less Bacteroidetes than the rats who experienced zero conflict. The microbiome of resilient rats, who displayed confidence in the face of adversity, more closely resembled that of relaxed rats.
The research team took it a step further and tested whether or not transplanting the bacteria of high-conflict rats into relaxed rats changed their behavior. They found that relaxed rats who received transplants from vulnerable rats started to show behavioral signs of depression.
Instantly download Gut Check, your guide to troubleshooting your gut imbalances.

Although this was a rat study, it gives a larger picture of how gut bacteria influence your mood and behavior. It’s not the first study of its kind — the body of knowledge around the gut-brain connection is expanding every day. You can read about how your gut bacteria control your mind here, and here’s an article about the connection between gut bacteria, stress, and mood.
One of the best things you can do for your physical and mental health is to fix leaky gut, a condition where certain overgrowths lead to weak spots in intestinal walls, and to encourage a diversified gut microbiome. Here’s how to get started.
by Dave Asprey
by Dave Asprey
[tldr]
[/tldr]
I’ve tried every diet known to man, from raw vegan to strictly meat, eggs, and butter. At the time, I was fat, sick, and slow, and I wanted to find the magic pill to feeling human again.
After a lot of frustrating trial-and-error, I can now say without a shadow of a doubt that a low-inflammation ketogenic diet like the Bulletproof Diet is a powerful way to shed body fat and dial in your brain power.
Getting into ketosis with diet alone isn’t fun. You have a period of a few days to two weeks when your body clamors for carbs and you feel like crap. To get through that period and then to amplify results once in ketosis, people have been experimenting with exogenous ketones — ketone supplements.
Keep reading to find out the difference between ketone esters and ketone salts, and the third exogenous ketone option that will get you into ketosis faster.

Your liver starts making ketones for two main reasons. If you’re diabetic, you make ketones when you don’t have enough insulin to get energy out of the glucose in your bloodstream. When ketones climb too high, diabetics go into ketoacidosis, which can be life-threatening.
For everyone else, you start making ketones when you:
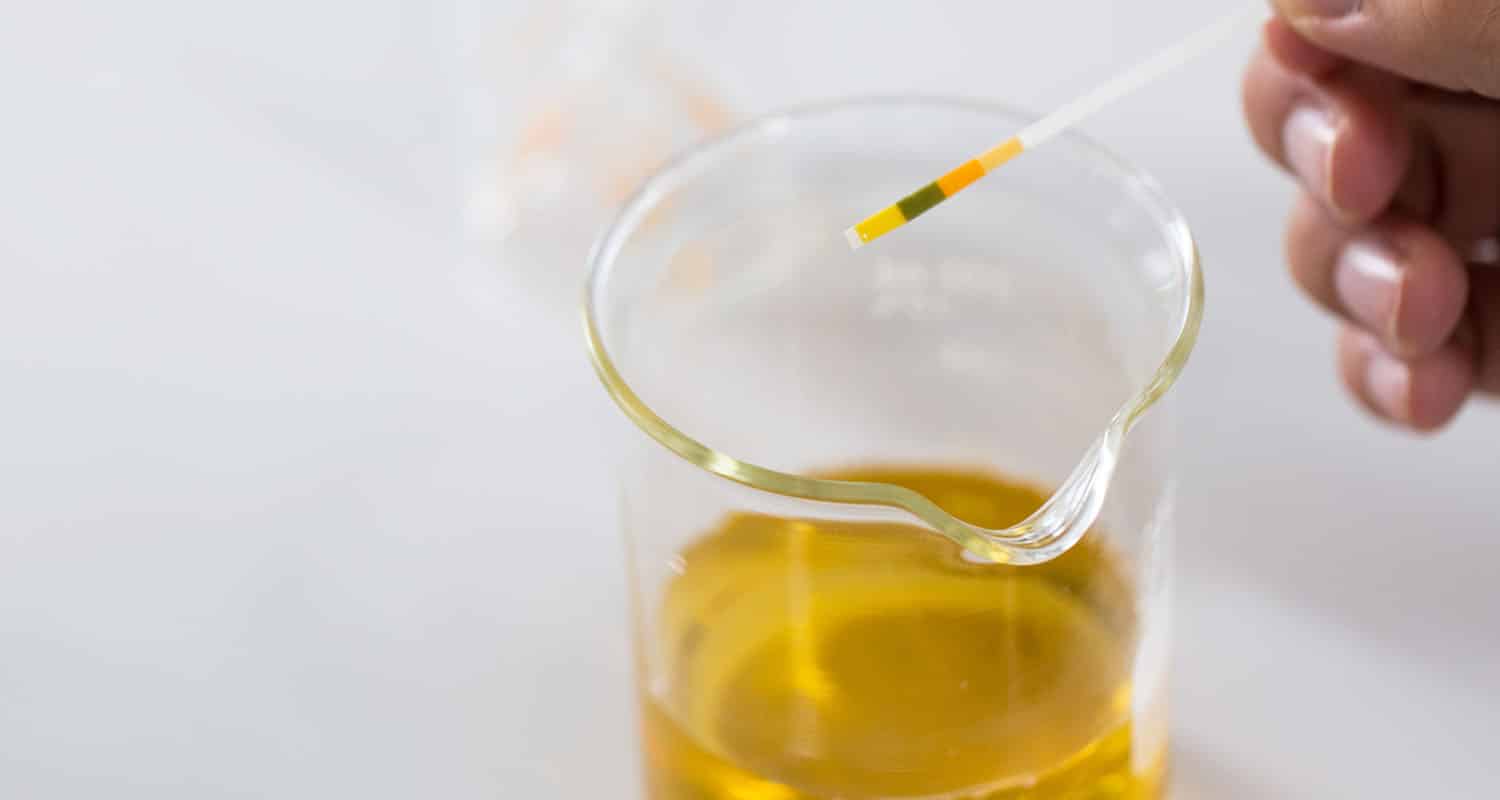

When you urine test your ketone levels, you’re measuring AcAc.
In your liver, two acetyl CoA molecules (think delivery truck molecules for energy packages), will hook up to make one acetoacetate ketone body. Rinse and repeat, until your hunger quiets down and you feel your energy shoot through the roof.
From there, acetoacetate will either:
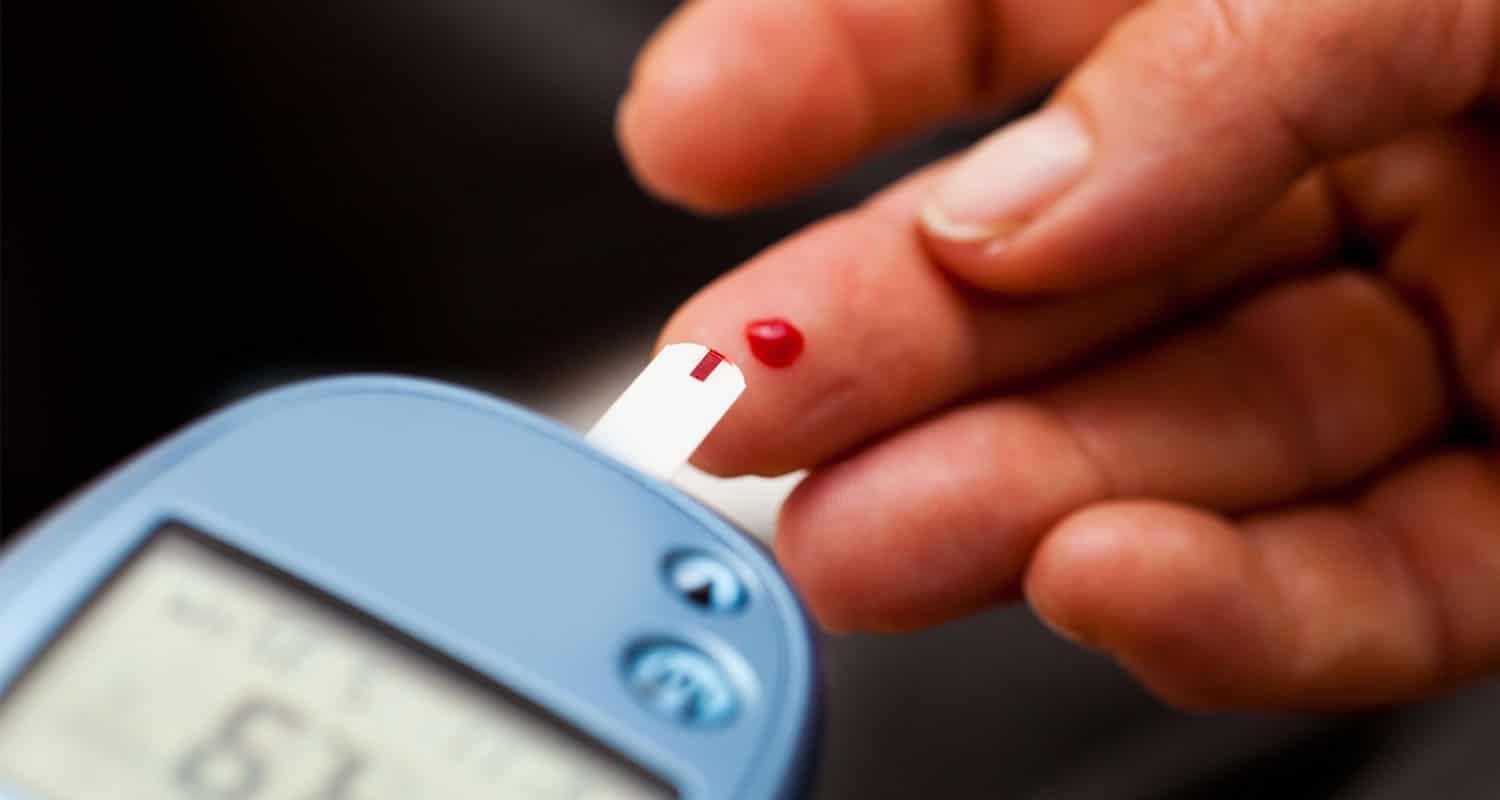
Some brands of urine test strips claim they’re measuring BHB, but they’re actually using your AcAc levels to approximate your BHB levels. Test strips don’t detect BHB at all, though, so it’s not an exact indicator. Since BHB is #ketogoals, get yourself a blood keto meter and test the real thing.
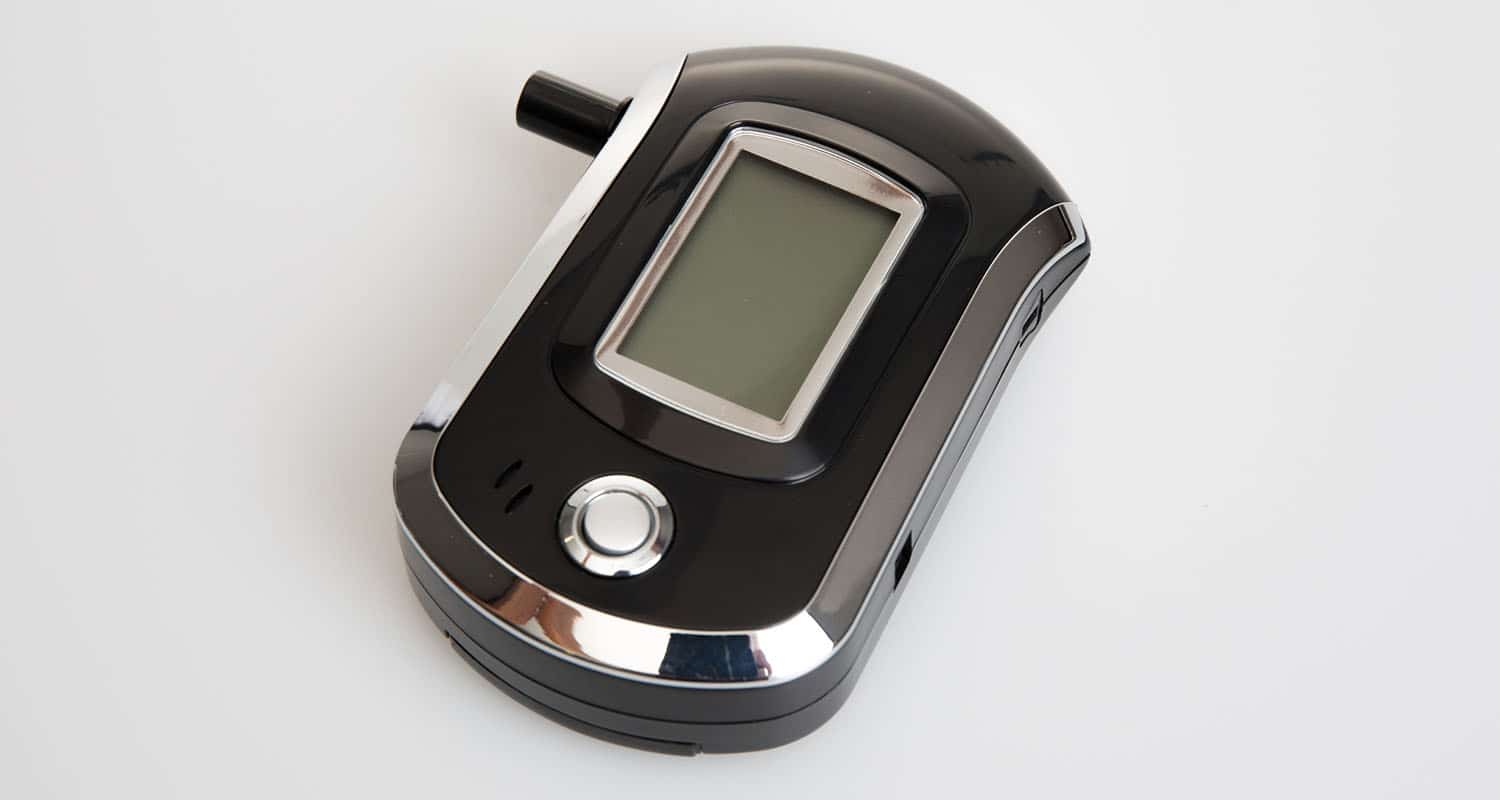
When you measure ketones using a ketone breath analyzer, you’re detecting acetone. Again, the goal is BHB, and acetone is a proxy measure for BHB.

Whether you want to sidestep the misery of the keto flu, take a shortcut to all of the amazing benefits of ketosis, or you want to ramp up the results you’ve seen already, you’ve started looking at hacks for getting your ketone levels up faster than you would on your own. So, do you supplement? Here are your options, and keep reading to find out why Brain Octane Oil is the safest and most effective exogenous ketone you’ll find anywhere.

Usually, you’ll find that manufacturers’ ketone body of choice is BHB, because it is more stable than AcAc, and because BHB is the ketone most available in the bloodstream when you’re naturally in deep ketosis.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16848698″]
Ketone salts were the first type of exogenous ketone available to the public. Early on, the keto community jumped all over the opportunity to boost ketones with a supplement, not knowing that there are problems with ketone salts. The main issue here is that they’re not bioidentical, which means your body may not use them the same way that they would use ketones that you made on board.
Since ketone bodies are attached to a mineral, they generally taste better and are easier to mask with flavor than ketone esters. Ketone salts raise your blood ketones, but they don’t raise your ketones as efficiently as ketone esters do.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5670148/”] Plus, ketone salts are still new to the supplement game, so we’re still learning about the effects — good and bad.
Instead of attaching to a mineral, ketone esters are ketone bodies, usually BHB, bound to 1,3 butanediol, an alcohol molecule that chemists happen to use to make polyurethanes. By the time they get into your bloodstream, ketone esters are chemically the same as the ketones your body makes, so your body knows what to do with them. Research shows that ketone esters raise your blood ketones far more efficiently than ketone salts do.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5670148/”]
Being bioidentical is a huge plus, but there are a couple major drawbacks to ketone esters. From a practical standpoint, ketone ester supplements are expensive — you’ll pay about $5 a day. If you make it past the sticker shock, you still have to deal with the taste factor. The taste is rough, and I mean rough. Imagine knocking back a fruity cough syrup that morphs into grandpa’s moonshine as you swallow. It’s like that.
Companies started making “ketones” out of fruits, namely raspberries, that are supposed to make you lose weight. Save yourself time and frustration, and wipe raspberry ketones from your radar. They’re not real.
Raspberry ketones are lab-created[ref url=”https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs00897960034a”] and not the same compound that your body recognizes or knows how to use. Plus, you need close to 100 lbs of raspberries to make one day’s worth of raspberry ketones. What a waste of delicious polyphenols.
If you tried raspberry ketones and your blood ketones went up, you’ve been duped. Some sneaky companies fake a rise in blood ketones by mixing MCT oil into their formula. The effect isn’t from raspberry ketones – it’s from the fat. More on why that works, coming up.
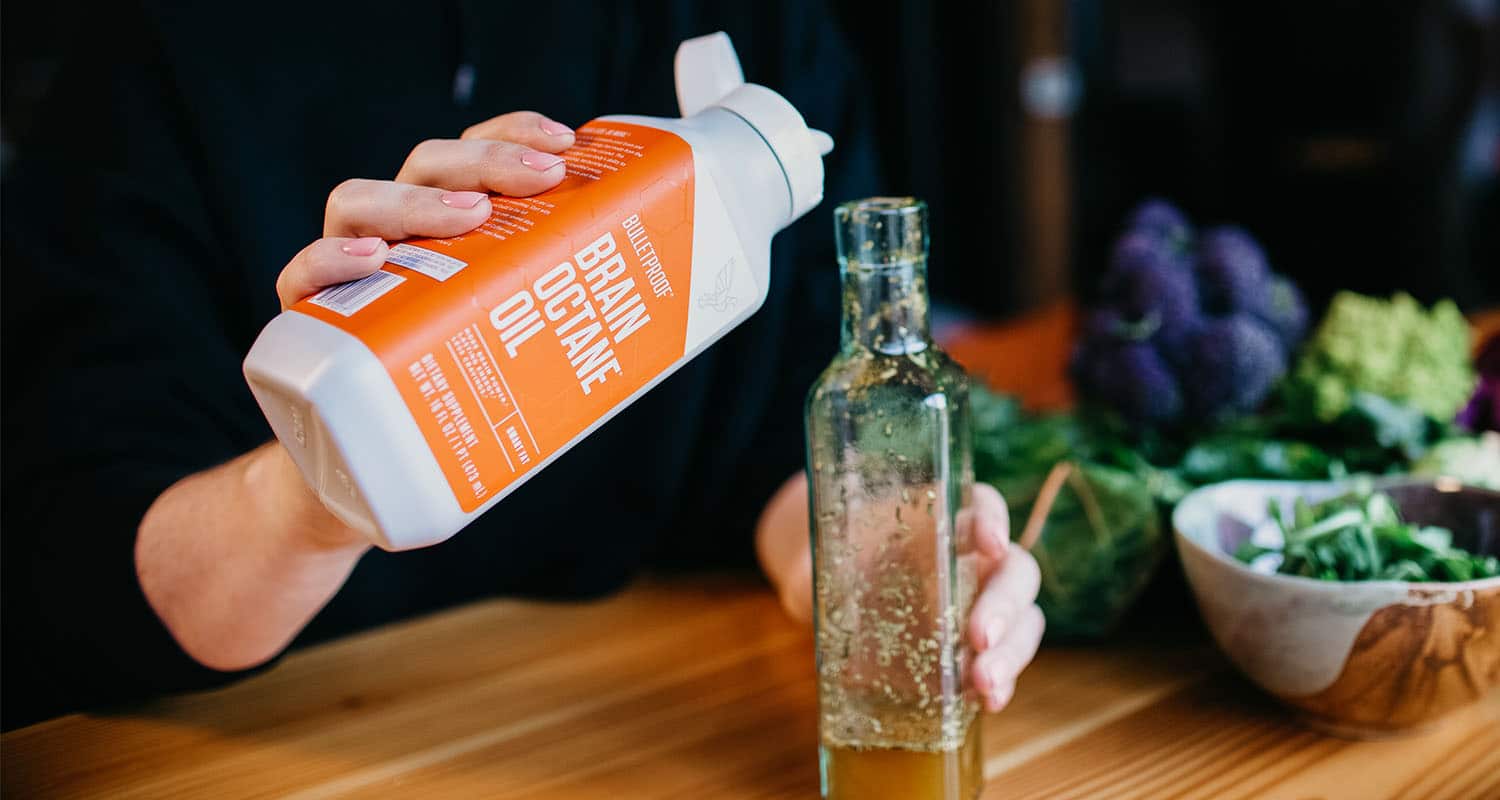

I’m talking about Brain Octane Oil. Brain Octane Oil is a coconut-derived medium-chain triglyceride that bypasses normal metabolism steps and converts directly into ketones that your body can use right away. It’s made of triple-distilled caprylic acid, which is so efficient at producing ketones that it raises ketones four times faster than diet alone. A UCSD study found that the type of medium-chain triglyceride that caprylic acid raised ketones more efficiently than any other type of MCT,[ref url=”https://academic.oup.com/cdn/article/1/4/e000257/4555134″] and Brain Octane Oil is 100% caprylic acid.
Because Brain Octane Oil is a fat, your body recognizes it as food and your metabolism knows exactly how to use it to make ketones.
Since brain Octane Oil is made from coconuts, you don’t have to worry about possible adverse reactions from a lab-created substance. Even better, it’s flavorless, and you can blend it into a delicious Bulletproof Coffee to power up your day.
Can you get a ketone boost with regular MCT oil? If you’re following a keto diet to the letter and you wake up fasted and take a generic MCT oil, you might see a moderate elevation in ketones.
Stick with the good stuff, though. Brain Octane Oil is pure caprylic acid, so it produces ketones more efficiently than other fat sources. It’s so efficient that it works even if you’ve had some carbs the night before.
First, no situation in nature would make that happen. If you went back a few centuries to your hunter-gatherer ways, ketones and glucose wouldn’t course through your bloodstream at the same time. You’re built to fuel with sugar first, then with ketones when you’re all out of sugar.
Second, having carbs and exogenous ketones in your bloodstream at the same time will likely give you the same glucose and insulin spikes and crashes as you would have with a standard diet, and the resulting hunger and distraction you aim to avoid. Except this time, you have ketones in your blood, too. Since there’s glucose available, you won’t flip your switch to the fat-burning state because your metabolism uses glucose first. As for the extra ketones in your system, you’re flushing your expensive supplement down the toilet — literally.
If you have the choice, and you do, burn fat for energy.

No matter who you are, you want to get to the other side as quickly as possible. Here’s how to get there without feeling hungry and slow.
If you follow these steps, you can shortcut right to the state of no cravings, intense focus, and incredible energy that you’ve been hearing all about. With the right tools and hacks at your disposal, you don’t have to suffer.
Receive weekly biohacking tips and tech by becoming a Dave Asprey insider.